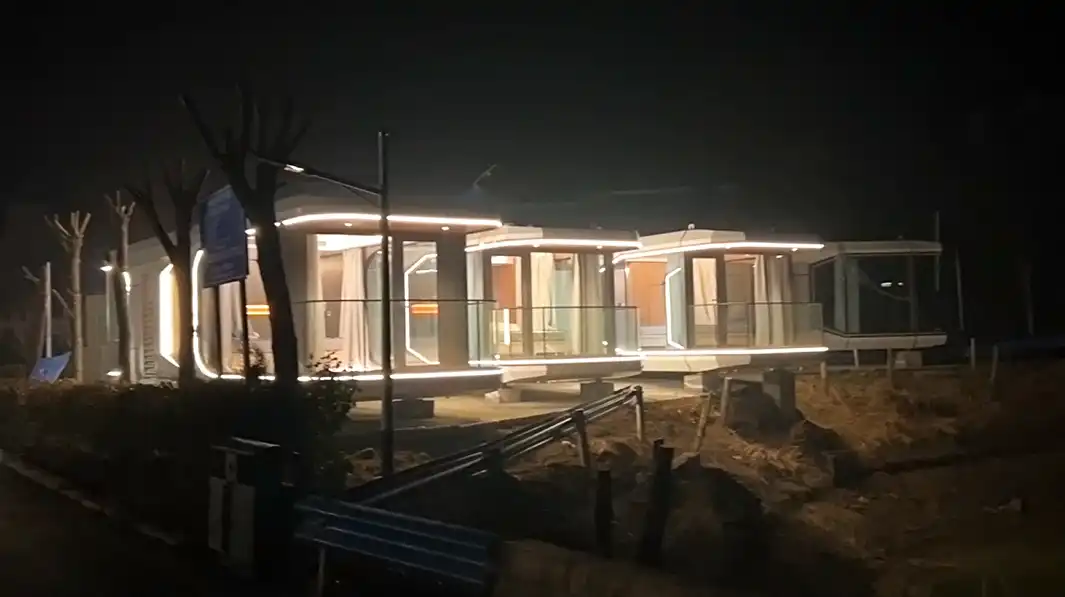
In the ever-evolving world of construction, thermal wall panels have emerged as a game-changer for builders and architects alike. These innovative panels offer a perfect blend of efficiency, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making them an ideal choice for both residential and commercial projects. As the demand for energy-efficient buildings continues to rise, thermal wall panels are becoming increasingly popular due to their superior insulation properties and quick installation process. Let's delve into the world of these revolutionary building materials and discover how they're transforming the construction industry.
The Evolution of Thermal Wall Panels in Modern Construction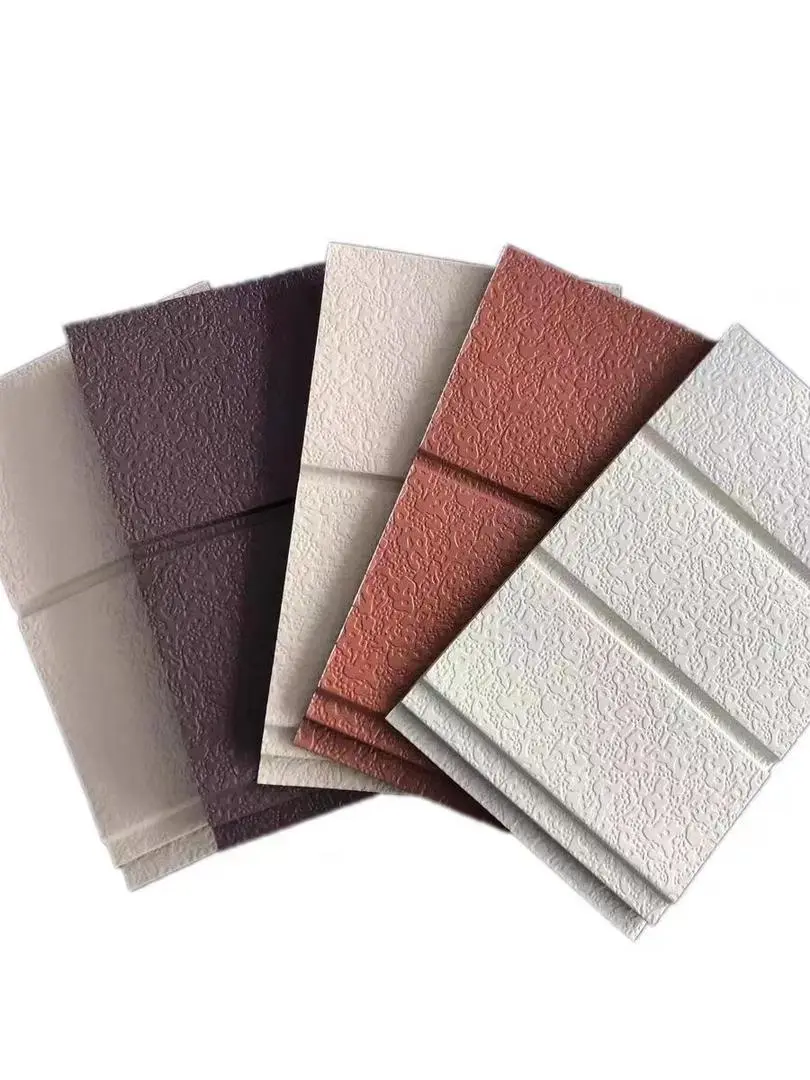
Understanding the Basics of Thermal Wall Panels
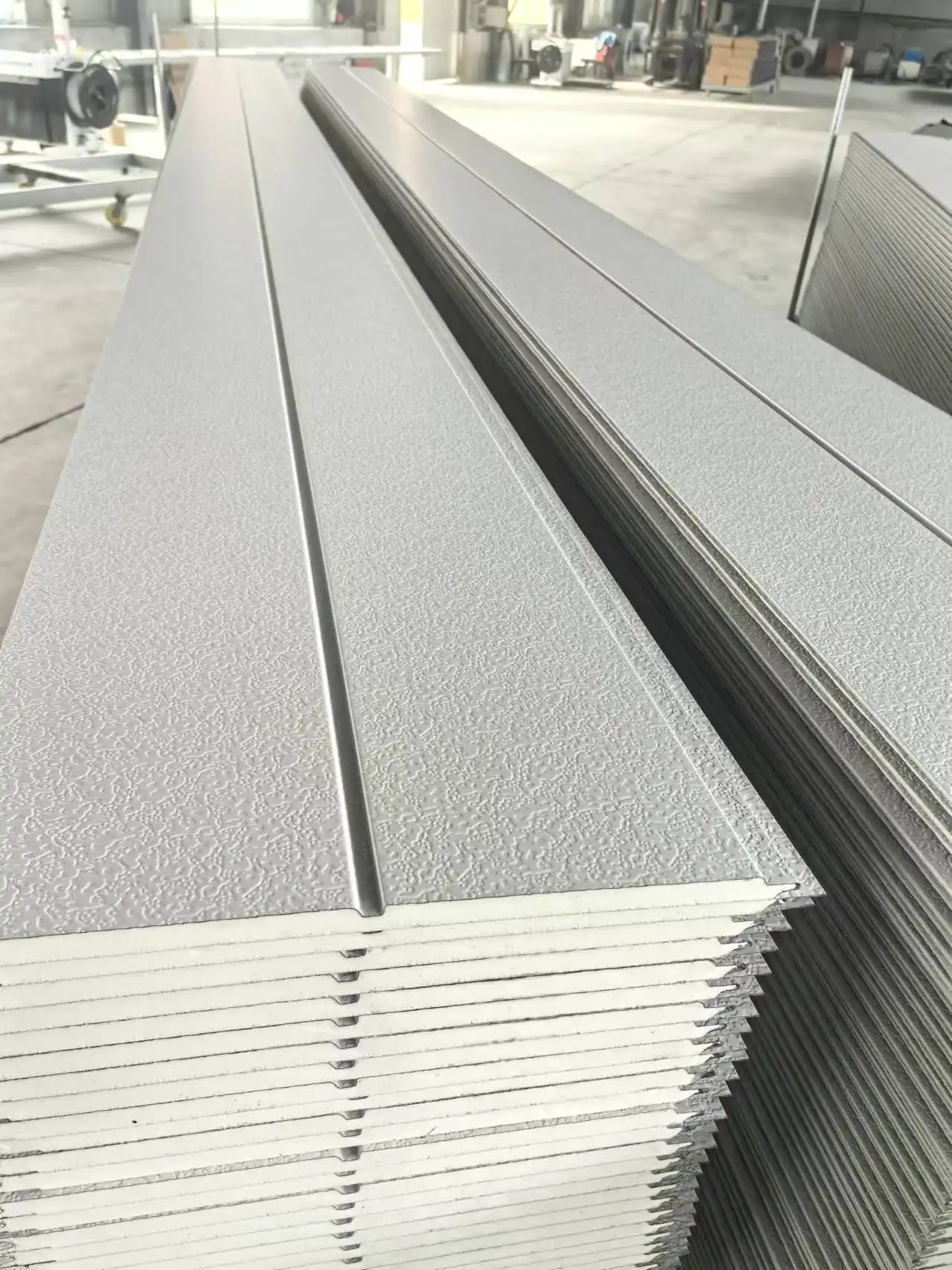
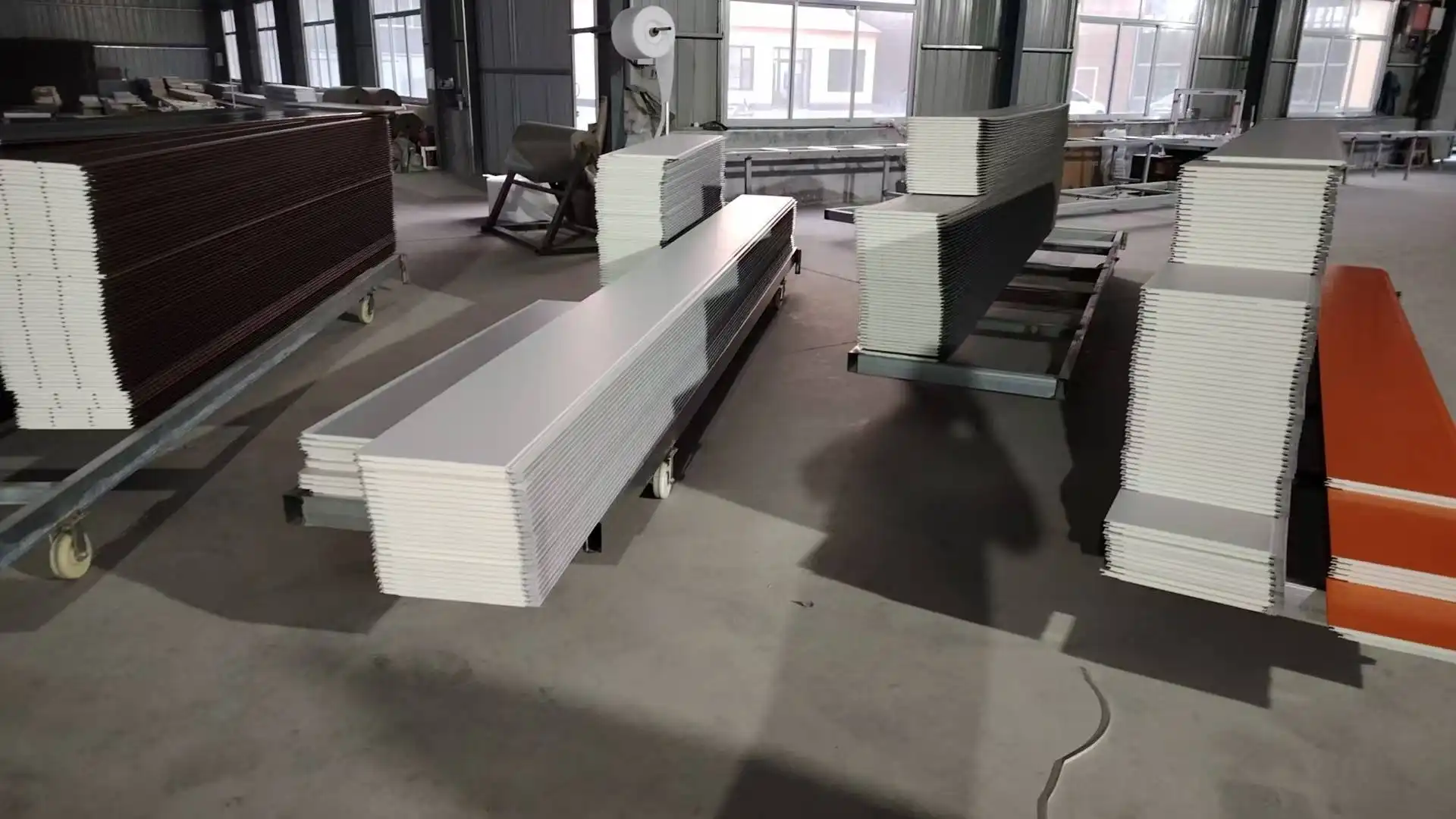
Thermal wall panels are advanced building components designed to provide excellent insulation while serving as structural elements. These panels typically consist of a core insulation material sandwiched between two layers of durable facing. The core is often made of materials like polyurethane or rock wool, known for their exceptional thermal resistance properties. The outer layers can be composed of various materials, including steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, depending on the specific requirements of the project.
As a thermal wall panels manufacturer, Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. has been at the forefront of developing these innovative products. Our thermal wall panels are engineered to meet the highest standards of energy efficiency, durability, and aesthetic versatility. We offer a range of thickness options (50mm, 75mm, 100mm) and size options (1200mm x 2400mm or custom sizes) to suit diverse project needs.
The Rise of Thermal Wall Panels in Sustainable Architecture
The growing emphasis on sustainable building practices has significantly contributed to the popularity of thermal wall panels. These panels play a crucial role in reducing a building's carbon footprint by minimizing energy consumption for heating and cooling. The superior insulation provided by thermal wall panels helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, reducing the load on HVAC systems and consequently lowering energy costs.
Moreover, thermal wall panels are often made from recyclable materials, aligning with green building initiatives. At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we prioritize sustainability in our manufacturing processes, ensuring that our thermal wall panels contribute to eco-friendly construction practices.
Advancements in Thermal Wall Panel Technology
Recent years have seen significant advancements in thermal wall panel technology. Manufacturers are constantly innovating to improve the performance and versatility of these panels. Some of the latest developments include:
- Enhanced fire-resistant properties, with panels achieving Class A and Class B fire ratings
- Improved weather resistance, including UV and corrosion resistance
- Integration of smart technologies for better monitoring and control of thermal performance
- Development of panels with higher R-values for superior insulation
As a leading thermal wall panels manufacturer, we at Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. are committed to staying at the cutting edge of these technological advancements. Our thermal wall panels incorporate the latest innovations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Benefits of Using Thermal Wall Panels in Construction Projects
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the primary advantages of thermal wall panels is their exceptional energy efficiency. The high-performance insulation core in these panels significantly reduces heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a building. This results in lower energy consumption for heating and cooling, leading to substantial cost savings over time.
Our thermal wall panels are designed with energy efficiency as a top priority. The polyurethane or rock wool insulation cores we use offer superior thermal resistance, helping to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures year-round. This not only reduces energy bills but also contributes to a building's overall sustainability profile.
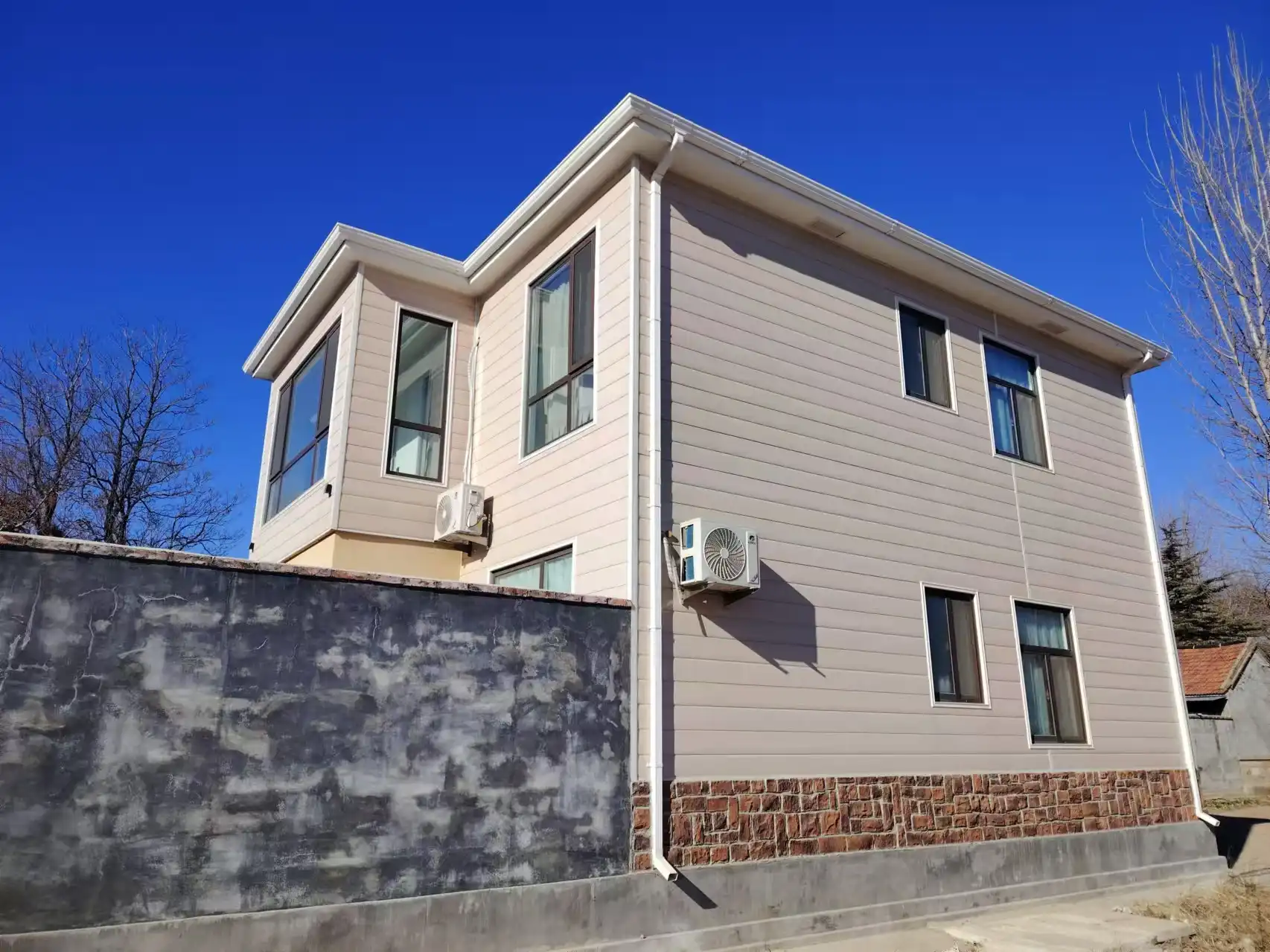
Rapid Installation and Reduced Labor Costs
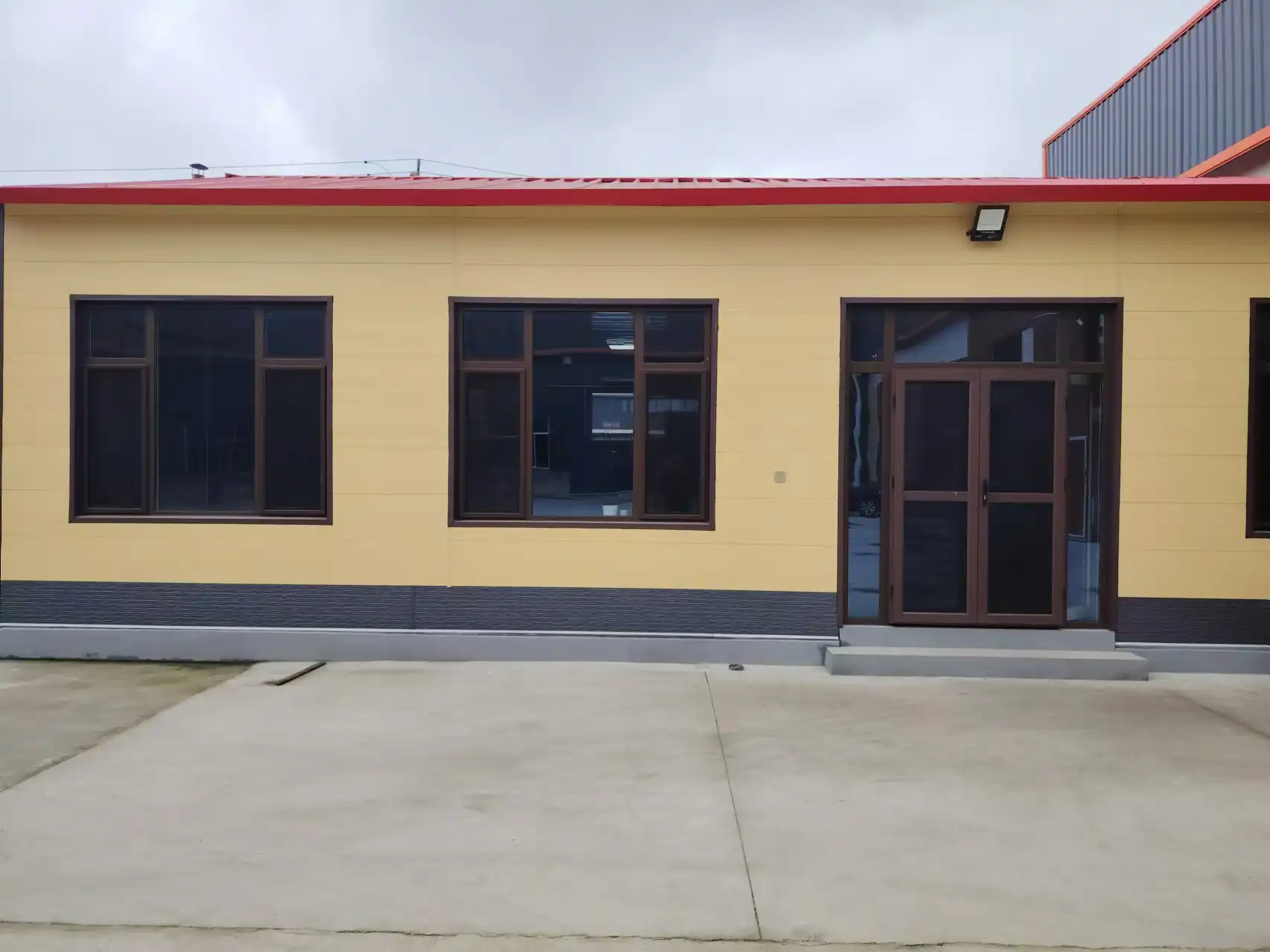
Thermal wall panels are renowned for their ease of installation, which can significantly speed up construction timelines. The modular nature of these panels allows for quick and straightforward assembly, reducing on-site labor requirements and associated costs. This is particularly beneficial for large-scale projects or those with tight deadlines.
At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we've optimized our thermal wall panels for easy installation. Our panels feature a user-friendly design that allows for seamless integration into various building structures. This not only accelerates the construction process but also minimizes the potential for errors during installation.
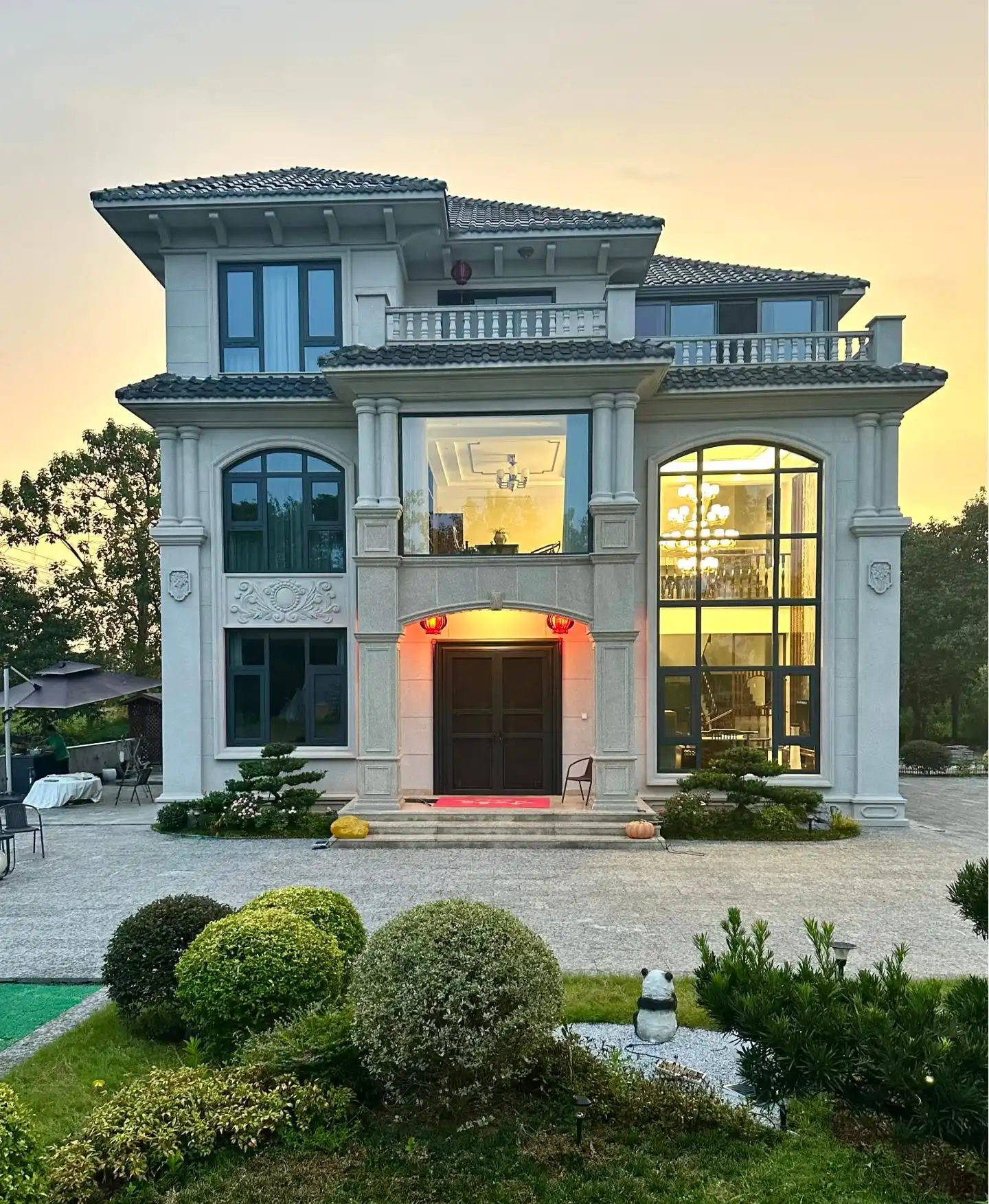
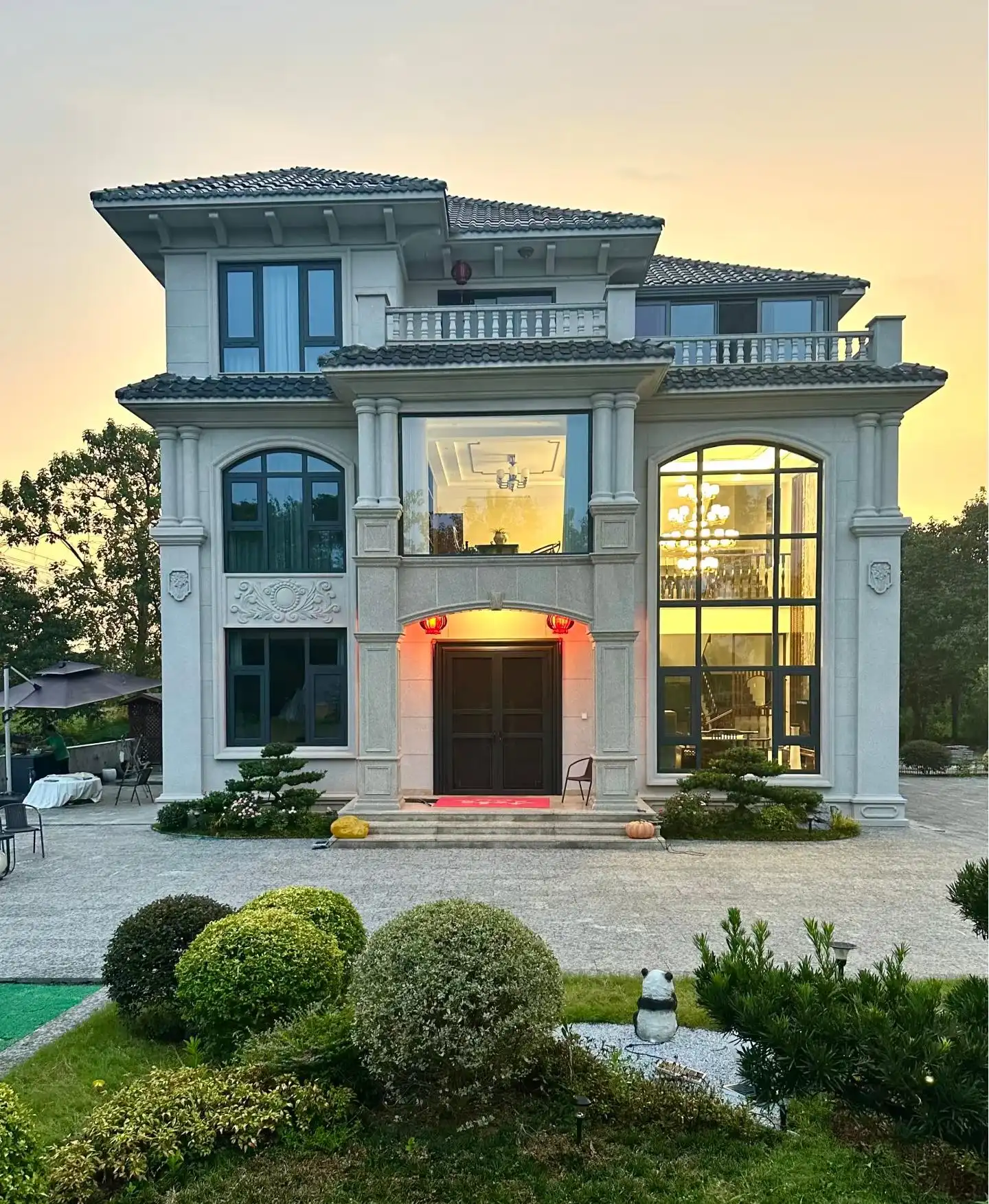
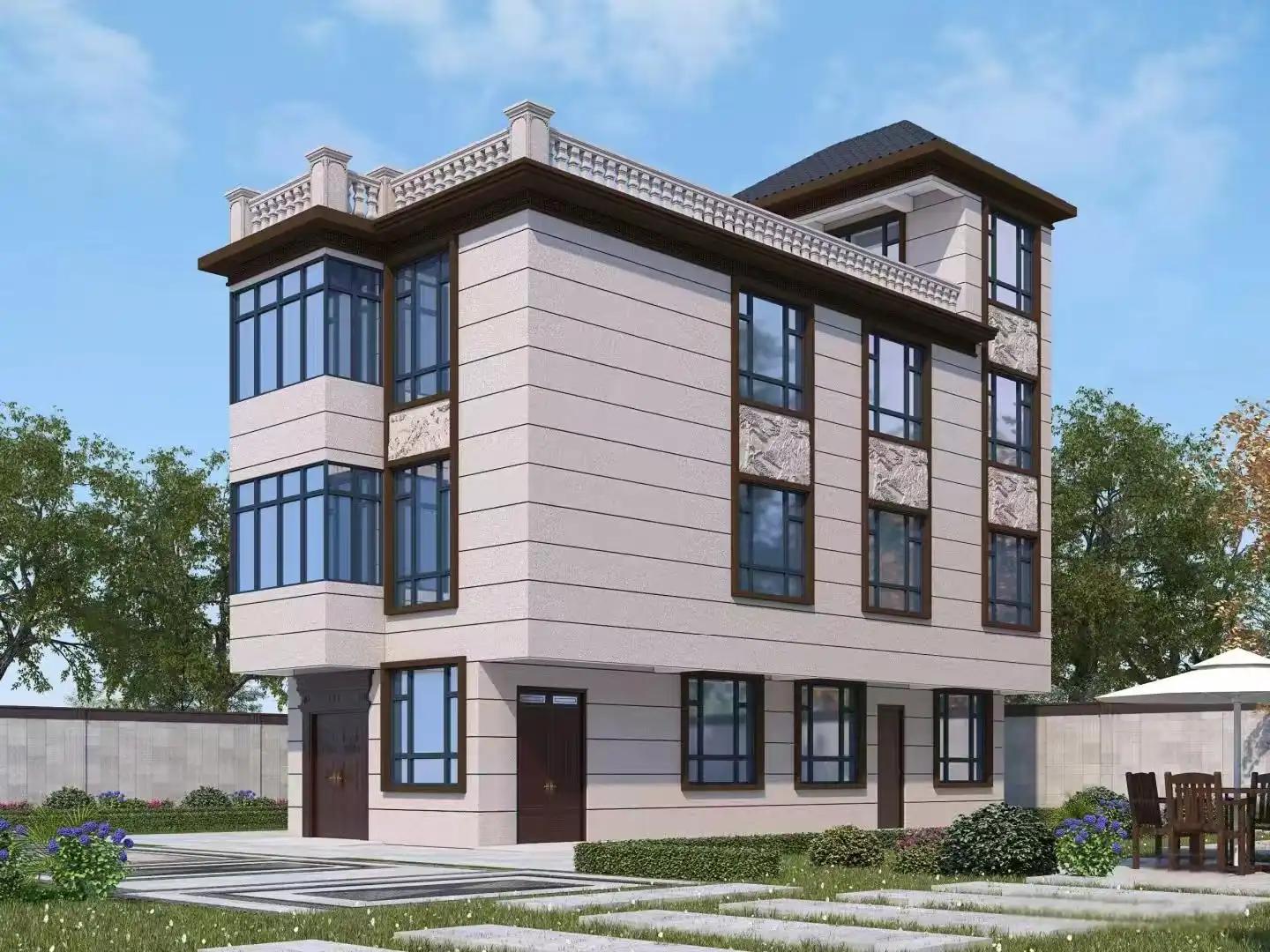
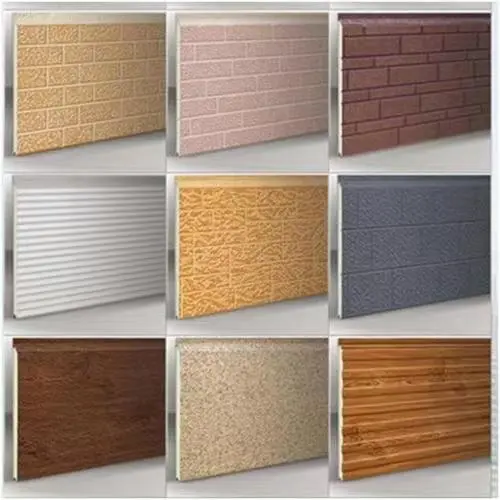
Versatility in Design and Aesthetics
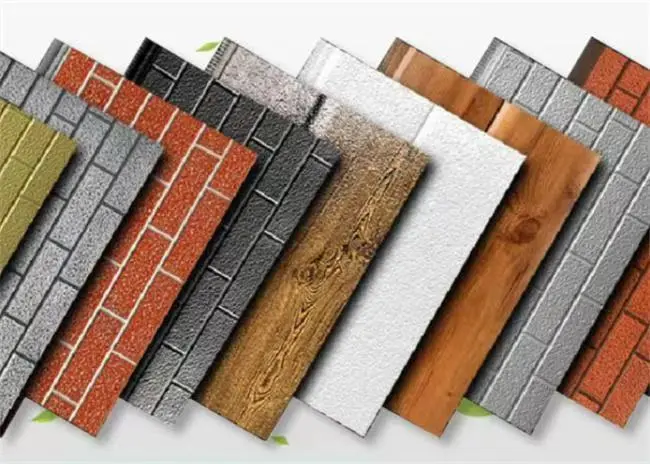
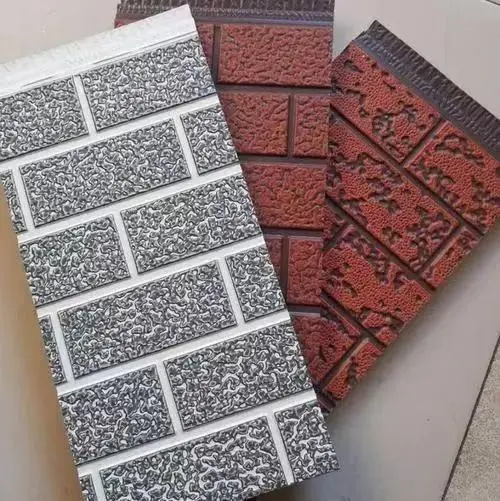
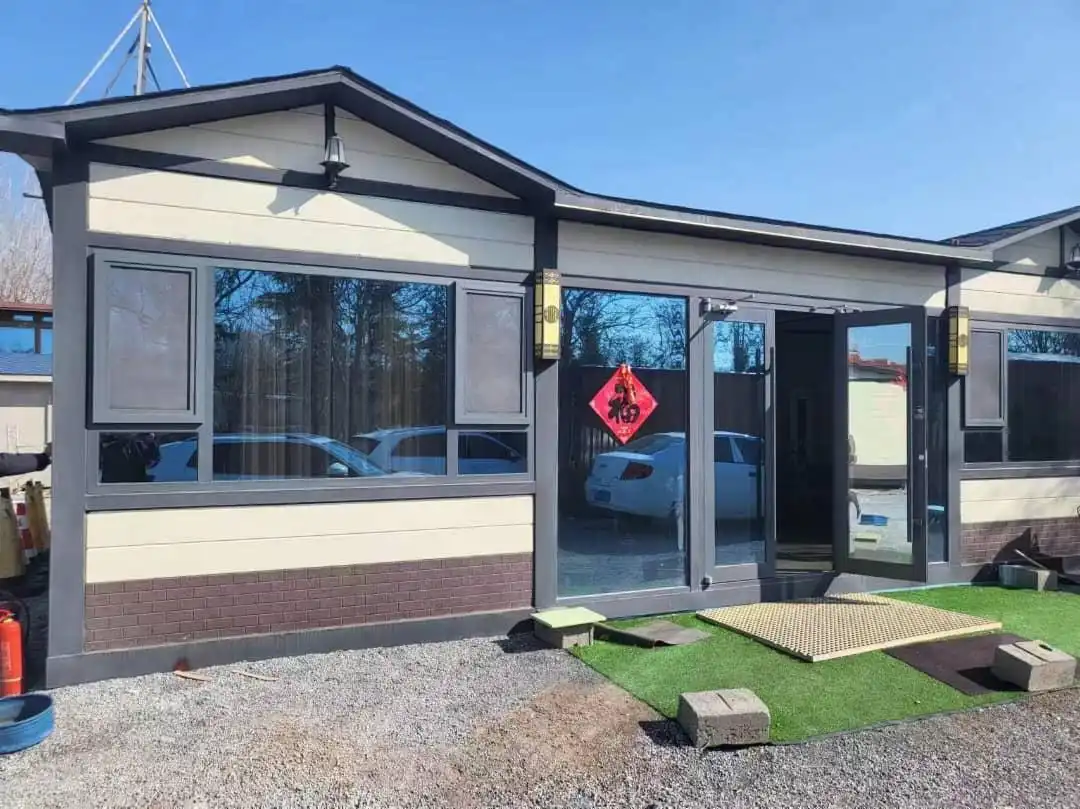
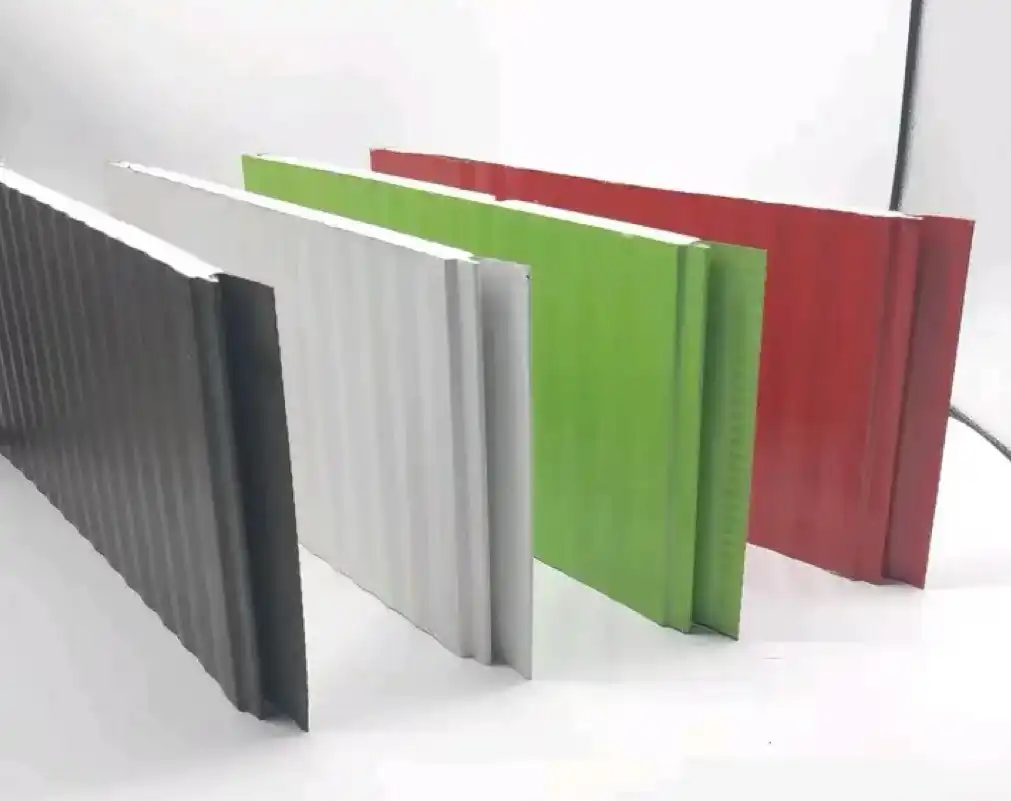
Thermal wall panels offer remarkable versatility in terms of design and aesthetics. They come in a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes, allowing architects and designers to achieve their desired look without compromising on performance. This flexibility makes thermal wall panels suitable for various architectural styles, from modern minimalist designs to more traditional aesthetics.
Our thermal wall panels are available in an extensive range of colors, including options from the RAL color chart and custom colors to match specific project requirements. We also offer various surface finishes and textures, ensuring that our panels can meet diverse aesthetic needs while maintaining their superior thermal performance.
Choosing the Right Thermal Wall Panels for Your Project
Factors to Consider When Selecting Thermal Wall Panels
When choosing thermal wall panels for a construction project, several factors need to be considered:
1.Insulation requirements: Determine the R-value needed based on local climate and building codes.
2.Structural performance: Consider the load-bearing capabilities of the panels.
3.Fire resistance: Ensure the panels meet or exceed local fire safety standards.
4.Moisture resistance: Choose panels that can withstand local weather conditions.
5.Aesthetics: Select panels that align with the overall design vision of the project.
As a reputable thermal wall panels manufacturer, we offer a range of options to meet these diverse requirements. Our panels are engineered to provide optimal insulation, structural integrity, and fire resistance while offering flexibility in design.
Understanding Technical Specifications of Thermal Wall Panels
To make an informed decision, it's crucial to understand the technical specifications of thermal wall panels. Key parameters to look for include:
- Thermal conductivity (K-value)
- Thermal resistance (R-value)
- Fire rating
- Sound insulation properties
- Wind load resistance
- Water vapor permeability
At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we provide comprehensive technical data for all our thermal wall panels. Our products are tested to meet international standards such as ISO, CE, and UL, ensuring reliability and performance.
Working with a Thermal Wall Panels Manufacturer
Collaborating with an experienced thermal wall panels manufacturer can greatly benefit your construction project. A reputable manufacturer can offer:
- Expert advice on panel selection based on project requirements
- Custom manufacturing options to meet specific needs
- Technical support during installation and beyond
- Quality assurance and warranty support
As a leading thermal wall panels manufacturer, Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. offers comprehensive support throughout your project. From initial consultation to post-installation support, our team of experts is committed to ensuring the success of your construction endeavor.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Thermal wall panels represent a significant advancement in construction technology, offering a perfect blend of energy efficiency, rapid installation, and design flexibility. These innovative building components are transforming the way we approach both residential and commercial construction projects. By providing superior insulation, reducing construction times, and offering versatile aesthetic options, thermal wall panels are proving to be an invaluable asset in modern building practices.
Are you ready to elevate your next construction project with high-performance thermal wall panels? Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. is here to help. As a leading thermal wall panels manufacturer, we offer a wide range of products designed to meet your specific needs. Contact us today at info@sdqsc.com to learn more about our thermal wall panels and how they can benefit your construction project. Let's build a more energy-efficient and sustainable future together!
FAQs
What are the main advantages of using thermal wall panels in construction?
Thermal wall panels offer superior insulation, quick installation, cost-effectiveness, and design versatility. They help reduce energy costs, speed up construction timelines, and provide excellent aesthetic options.
How do thermal wall panels contribute to energy efficiency?
Thermal wall panels have high insulation properties that minimize heat transfer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. This leads to lower energy consumption and costs.
Are thermal wall panels suitable for both residential and commercial projects?
Yes, thermal wall panels are versatile and can be used in various construction projects, including homes, offices, schools, and industrial buildings.
How long do thermal wall panels typically last?
With proper installation and maintenance, thermal wall panels can last for several decades, often matching or exceeding the lifespan of traditional building materials.
References
1.International Energy Agency. (2021). "Buildings: A source of enormous untapped efficiency potential."
2.U.S. Department of Energy. (2022). "Insulation."
3.American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers. (2021). "ASHRAE Handbook - Fundamentals." Atlanta: ASHRAE.
4.National Institute of Building Sciences. (2022). "Whole Building Design Guide: Building Envelope."
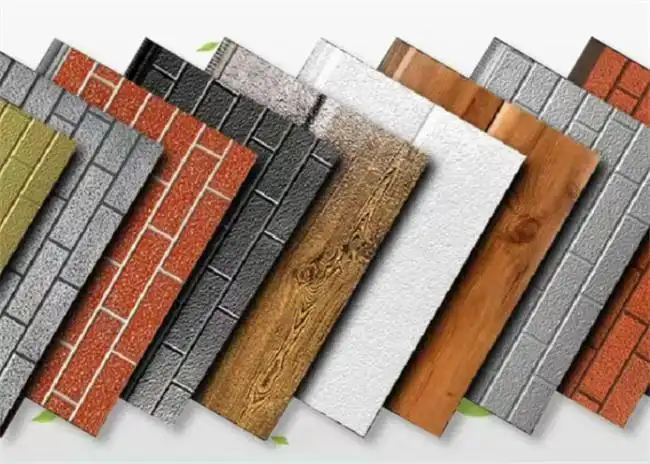
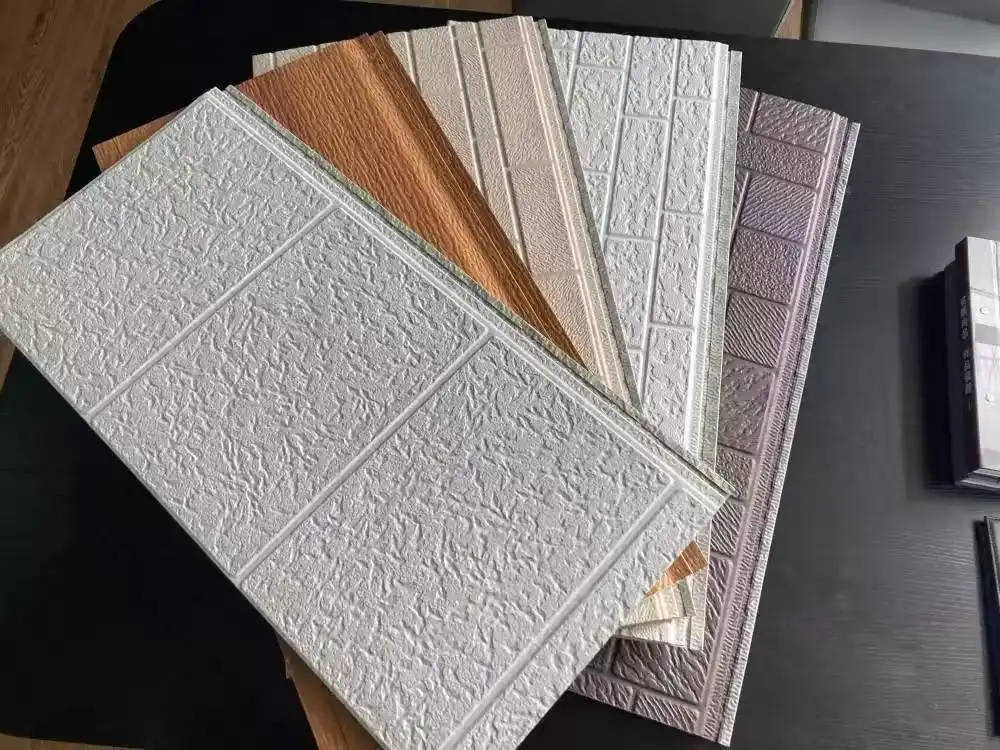



 Innovative Materials and Textures
Innovative Materials and Textures


 Conclusion
Conclusion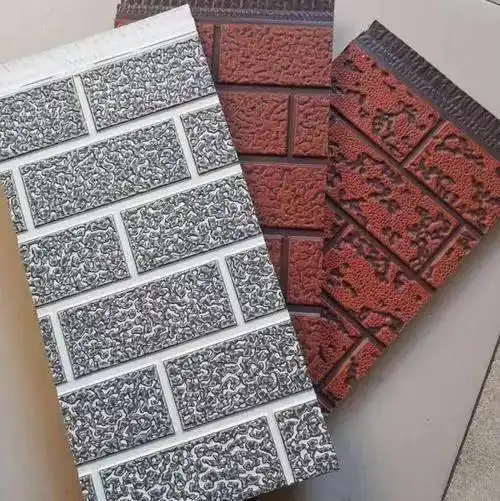




 FAQs
FAQs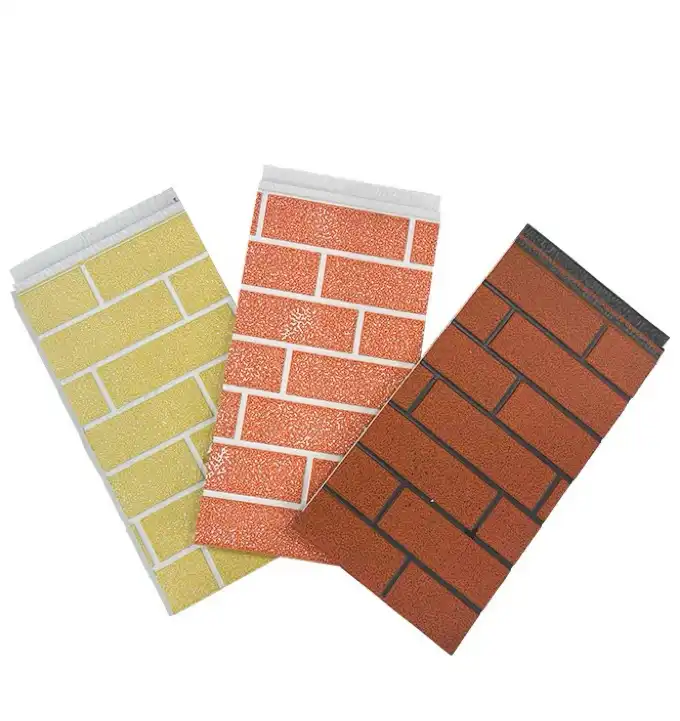
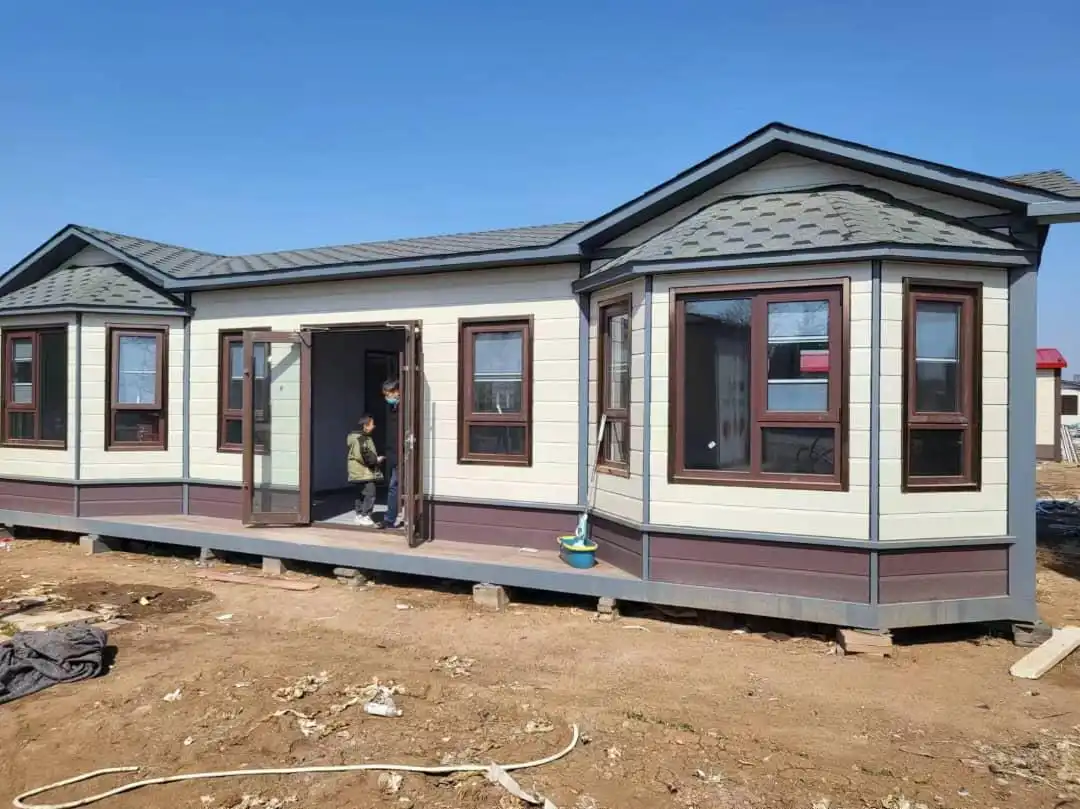

 Conclusion
Conclusion
 Thermal Performance: A Game-Changing Difference
Thermal Performance: A Game-Changing Difference
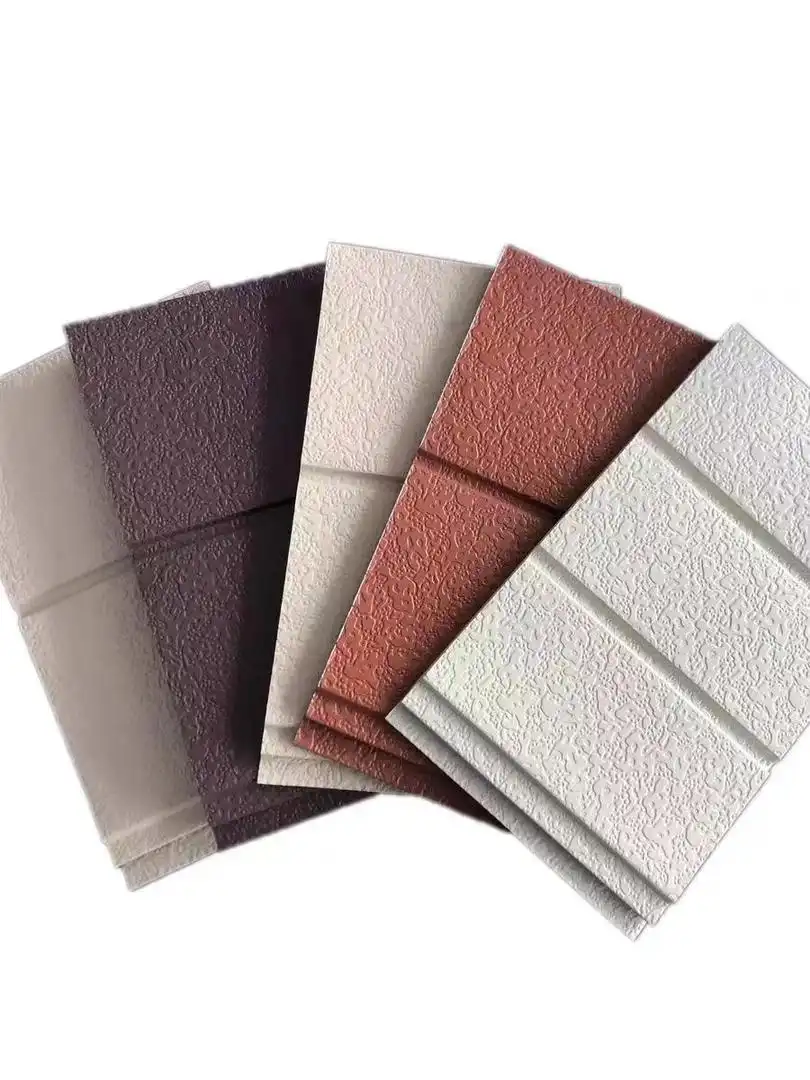





 FAQs
FAQs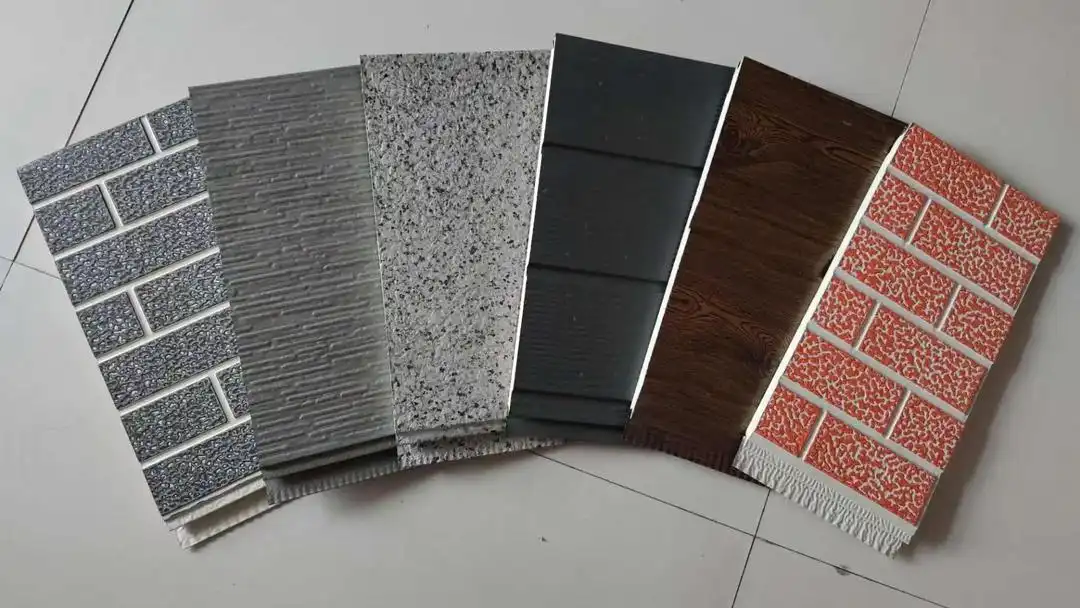




 Conclusion
Conclusion.webp)

