Understanding Prefabricated Thermal Panels and Their Benefits
Composition and Structure of Prefabricated Thermal Panels
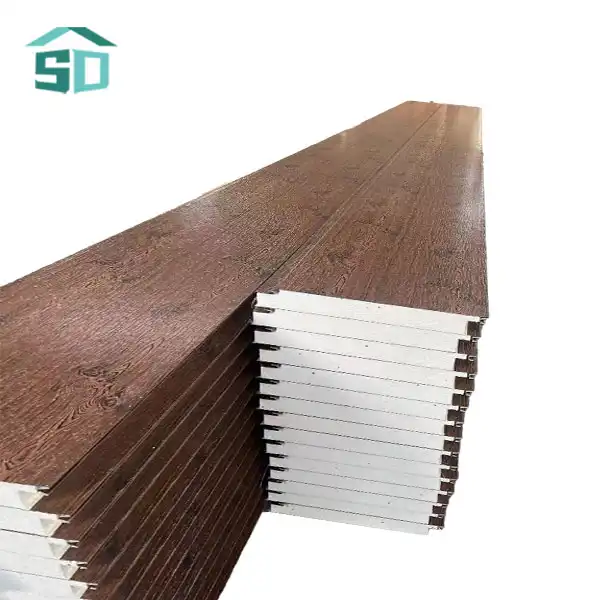
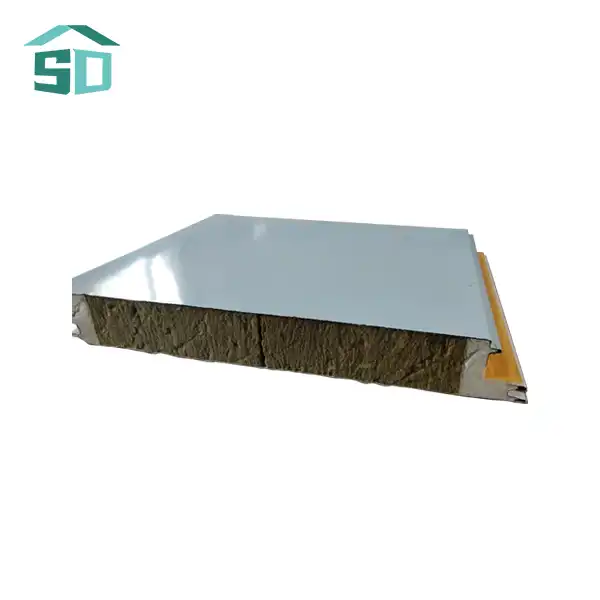
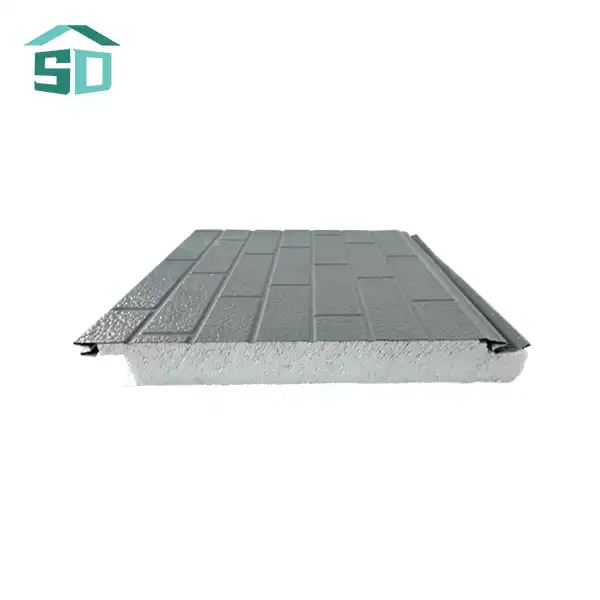
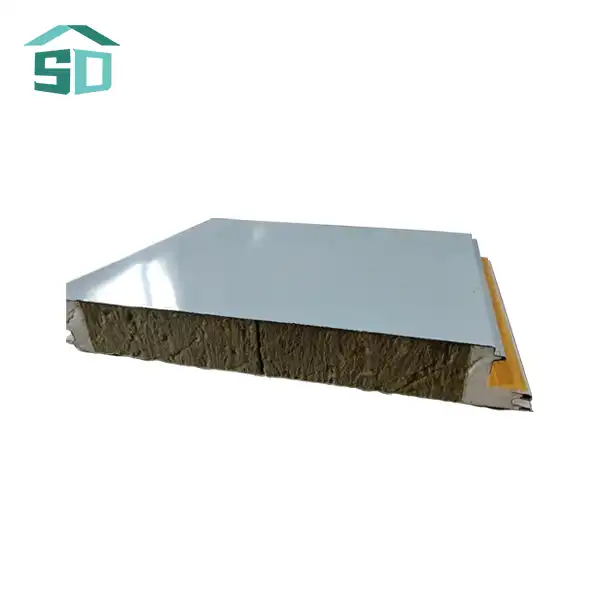
Prefabricated thermal panels are engineered building components designed to provide superior insulation and structural support. These panels typically consist of a core insulation material sandwiched between two facings. The core is often made of polyurethane foam, expanded polystyrene (EPS), or mineral wool, while the facings can be metal, such as steel or aluminum, or other materials like oriented strand board (OSB).
The unique structure of prefabricated thermal panels allows for excellent thermal performance. The insulation core minimizes heat transfer, while the rigid facings provide strength and durability. This composition results in a lightweight yet robust panel that can withstand various environmental conditions while maintaining its insulating properties.
Advantages of Using Prefabricated Thermal Panels in Construction
Prefabricated thermal panels offer numerous benefits that make them an attractive option for builders and architects:
- Energy Efficiency: The high insulation values of these panels significantly reduce heat loss or gain, leading to lower energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Quick Installation: Prefabricated panels can be rapidly installed, reducing on-site construction time and labor costs.
- Versatility: These panels can be used in various applications, from walls and roofs to floor systems, adapting to different architectural designs.
- Durability: High-quality prefabricated thermal panels are resistant to moisture, pests, and fire, ensuring long-term performance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial cost may be higher than traditional materials, the long-term energy savings and reduced maintenance needs often result in a lower overall lifecycle cost.
- Acoustic Performance: Many prefabricated thermal panels also provide sound insulation, enhancing the comfort of interior spaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Prefabricated Thermal Panels
Prefabricated thermal panels contribute to sustainable construction practices in several ways:
- Energy Conservation: By improving building envelope performance, these panels reduce the energy required for heating and cooling, lowering carbon emissions.
- Waste Reduction: Factory production of panels results in less on-site waste compared to traditional construction methods.
- Recyclability: Many components of prefabricated thermal panels can be recycled at the end of their life cycle, reducing landfill waste.
- Longevity: The durability of these panels extends the lifespan of buildings, reducing the need for frequent renovations or replacements.
Prefabricated thermal panels suppliers often prioritize sustainable manufacturing processes, using recycled materials and optimizing production to minimize environmental impact. This commitment to sustainability aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly building solutions in the construction industry.
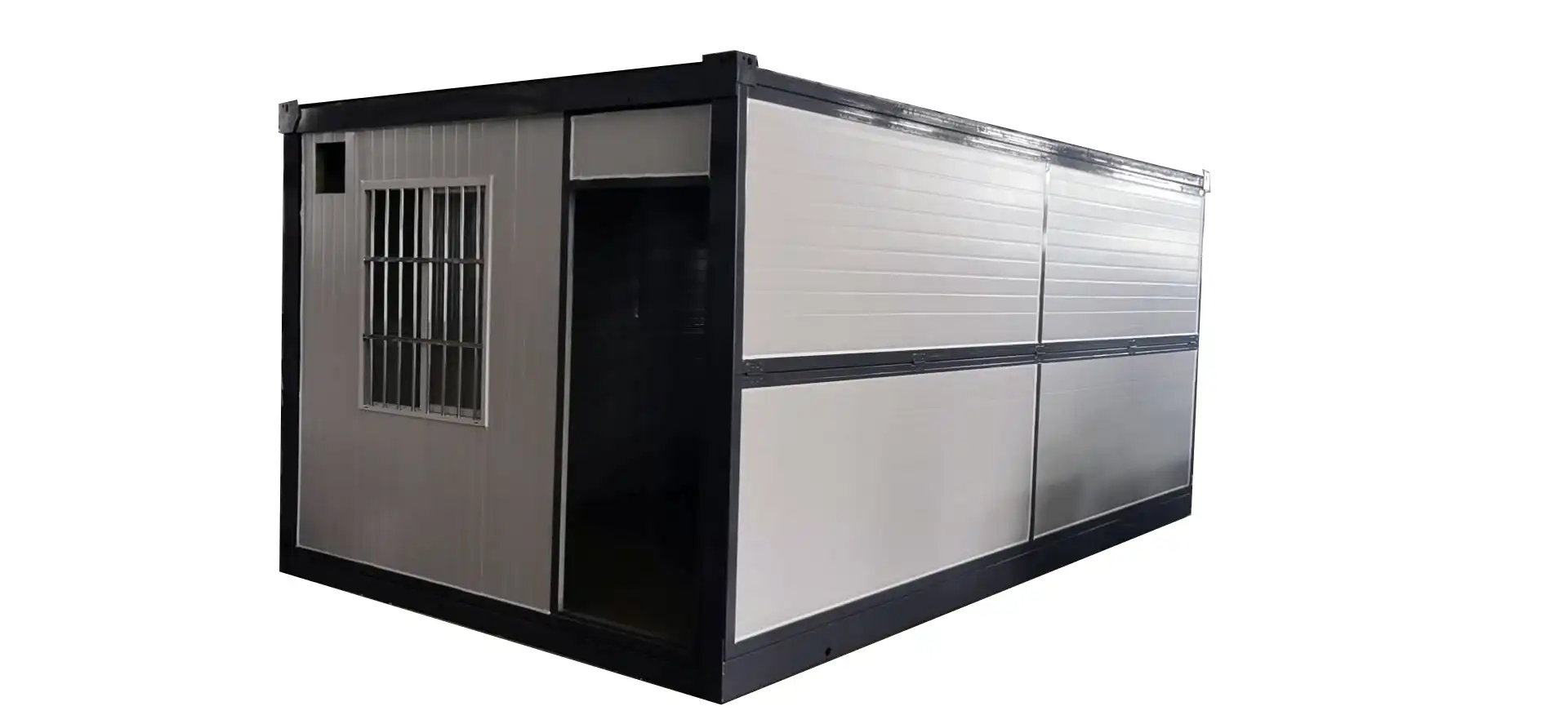
Applications of Prefabricated Thermal Panels in Various Sectors
Residential Construction: Enhancing Home Comfort and Efficiency
In the residential sector, prefabricated thermal panels have revolutionized home construction and renovation. These panels are extensively used for:
- Exterior Wall Systems: Prefabricated thermal panels provide excellent insulation for home exteriors, creating a thermal envelope that maintains comfortable indoor temperatures year-round.
- Roofing Solutions: As roofing materials, these panels offer superior insulation and weather protection, reducing attic heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter.
- Basement Insulation: Prefabricated thermal panels can effectively insulate basement walls, preventing moisture issues and improving energy efficiency.
- Garage Doors: Insulated garage doors made with these panels help maintain temperature control in attached garages, indirectly benefiting the home's overall energy performance.
The use of prefabricated thermal panels in homes not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to a more comfortable living environment by reducing drafts and maintaining consistent temperatures throughout the house.
Commercial and Industrial Applications: From Offices to Warehouses
The commercial and industrial sectors have embraced prefabricated thermal panels for their versatility and performance. Common applications include:
- Office Buildings: These panels are used in exterior walls and roofing systems of office complexes, providing energy-efficient solutions that reduce operational costs.
- Retail Spaces: Prefabricated thermal panels help create comfortable shopping environments while minimizing energy expenditure for heating and cooling large retail areas.
- Warehouses and Distribution Centers: The panels' insulation properties are crucial for maintaining specific temperature ranges in storage facilities, particularly for temperature-sensitive goods.
- Manufacturing Facilities: Industrial buildings benefit from the panels' ability to create controlled environments necessary for various manufacturing processes.
- Data Centers: The high insulation values of these panels help maintain the cool temperatures required for server rooms and data storage facilities.
In these applications, prefabricated thermal panels not only provide thermal insulation but also contribute to the structural integrity of the buildings, often serving as load-bearing elements in the construction.
Specialized Uses: Cold Storage, Agricultural, and Modular Construction
Prefabricated thermal panels find specialized applications in various niche sectors:
- Cold Storage Facilities: These panels are essential in creating and maintaining low-temperature environments for food storage, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive products.
- Agricultural Buildings: Barns, greenhouses, and livestock housing benefit from the insulation properties of these panels, helping to maintain optimal conditions for plants and animals.
- Modular Construction: Prefabricated thermal panels are integral to modular building systems, allowing for rapid assembly of temporary or permanent structures in remote locations or for disaster relief efforts.
- Sports Facilities: Indoor sports arenas and ice rinks use these panels to maintain specific temperature and humidity levels necessary for various sporting activities.
- Clean Rooms: In pharmaceutical and technology industries, these panels help create controlled environments with specific temperature, humidity, and air quality requirements.
The adaptability of prefabricated thermal panels to these specialized applications showcases their versatility and the broad range of industries that can benefit from their use.
Installation Considerations and Best Practices
Preparing for Installation: Site Assessment and Planning
Before installing prefabricated thermal panels, thorough site assessment and planning are crucial:
- Structural Evaluation: Ensure the existing structure can support the weight of the panels and any additional loads.
- Climate Considerations: Assess local climate conditions to determine the optimal insulation values and panel specifications.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local building codes and ensure compliance with fire safety and energy efficiency standards.
- Moisture Management: Plan for proper moisture barriers and ventilation to prevent condensation issues.
- Panel Layout: Design an efficient panel layout to minimize waste and optimize thermal performance.
Proper planning not only ensures a smooth installation process but also maximizes the benefits of using prefabricated thermal panels in the construction project.
Installation Techniques for Different Applications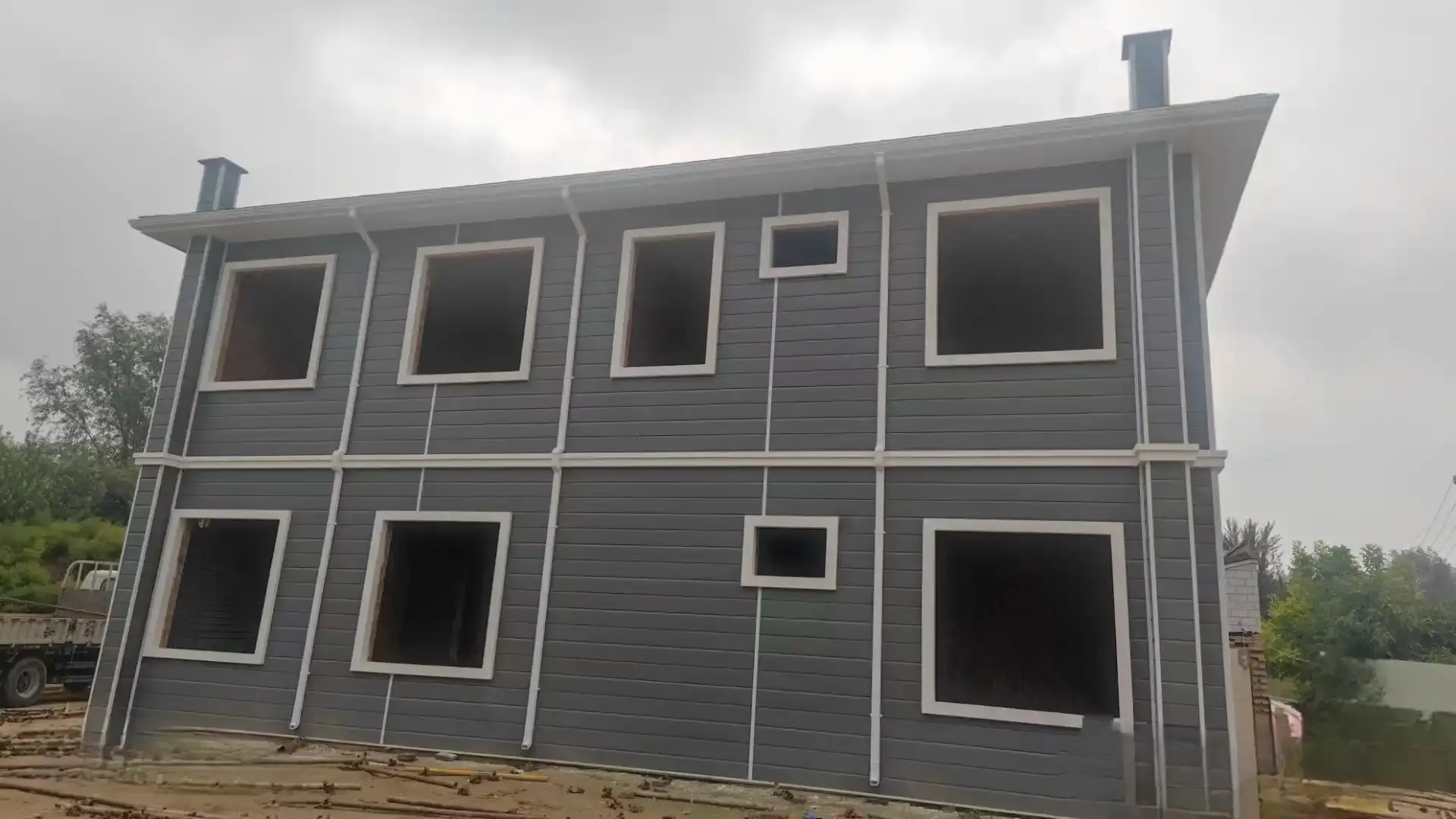
The installation of prefabricated thermal panels varies depending on the application:
- Wall Systems: Panels are typically installed vertically, secured to the building frame using specialized fasteners. Proper sealing of joints is crucial for maintaining the thermal barrier.
- Roofing Applications: Roof panels are often installed with a slight slope to ensure proper drainage. Special attention is given to ridge caps and eave details to prevent water infiltration.
- Floor Systems: When used in flooring, panels are installed over a subfloor or directly onto floor joists, with careful consideration given to load-bearing capacity.
- Cold Storage: Installation in cold storage facilities requires meticulous attention to sealing and vapor barriers to maintain temperature control and prevent moisture issues.
Regardless of the application, proper alignment, secure fastening, and effective sealing of joints are critical for optimal performance of prefabricated thermal panels.
Maintenance and Long-term Performance of Prefabricated Thermal Panels
To ensure the longevity and continued performance of prefabricated thermal panels:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic visual inspections to check for any signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or separation at joints.
- Cleaning: Keep panel surfaces clean to maintain their appearance and prevent the buildup of contaminants that could affect performance.
- Sealant Maintenance: Regularly inspect and replace sealants at joints and penetrations to maintain the integrity of the thermal barrier.
- Repair Promptly: Address any damage or issues promptly to prevent further deterioration or compromised performance.
- Monitor Energy Performance: Keep track of energy consumption to ensure the panels continue to provide expected insulation benefits.
With proper maintenance, prefabricated thermal panels can maintain their efficiency and structural integrity for many years, providing long-term value to the building.
Conclusion
Prefabricated thermal panels have emerged as a versatile and efficient solution in modern construction, offering applications across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Their superior insulation properties, coupled with ease of installation and durability, make them an attractive choice for builders and architects alike. From enhancing energy efficiency in homes to creating controlled environments in specialized facilities, these panels demonstrate remarkable adaptability. As the construction industry continues to prioritize sustainability and energy conservation, prefabricated thermal panels are poised to play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of building design and performance.
For those seeking high-quality prefabricated thermal panels and expert guidance on their application, Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. stands as a leading prefabricated thermal panels supplier. Our commitment to manufacturing excellence and customer satisfaction ensures that you receive products tailored to your specific needs. To explore how our prefabricated thermal panels can enhance your next construction project, please contact us at info@sdqsc.com.
FAQ
What are the main advantages of using prefabricated thermal panels in construction?
Prefabricated thermal panels offer several benefits, including excellent energy efficiency, quick installation, versatility in applications, durability, and long-term cost-effectiveness. They also contribute to sustainable building practices by reducing energy consumption and construction waste.
Can prefabricated thermal panels be used in both new construction and renovation projects?
Yes, these panels are suitable for both new builds and renovations. Their adaptability makes them ideal for upgrading existing structures or incorporating into new designs across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
How do prefabricated thermal panels contribute to a building's energy efficiency?
Prefabricated thermal panels provide superior insulation, significantly reducing heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors. This improved thermal performance leads to lower energy requirements for heating and cooling, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower utility costs.
References
1. Building Science Corporation. (2021). "Thermal Performance of Prefabricated Panel Systems." Journal of Building Physics, 45(2), 112-128.
2. International Energy Agency. (2022). "Energy Efficiency in Buildings: The Role of Prefabricated Components." IEA Technology Report.
3. Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2020). "Advancements in Prefabricated Thermal Panel Technology." Construction and Building Materials, 215, 456-470.
4. U.S. Department of Energy. (2023). "Building Envelope and Insulation Guide." Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy.
5. World Green Building Council. (2022). "Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction." UNEP Publication.