The Science Behind Color and Heat Absorption
To understand how panel color affects heat absorption in PU insulated sandwich panels, we must first grasp the basic principles of color and light interaction. Different colors absorb and reflect varying amounts of solar radiation, which directly influences the heat absorption properties of materials.
Light Absorption and Reflection
When sunlight hits a surface, some wavelengths are absorbed while others are reflected. The color we perceive is a result of the reflected wavelengths. Darker colors tend to absorb more light across the visible spectrum, while lighter colors reflect more. This phenomenon has significant implications for the thermal performance of PU insulated sandwich panels.
The Role of Albedo
Albedo, or solar reflectance, is a measure of how much solar radiation is reflected by a surface. Lighter colors have a higher albedo, meaning they reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat. Conversely, darker colors have a lower albedo, absorbing more solar energy and converting it to heat. When considering PU insulated sandwich panels, the albedo of the exterior facing can significantly impact the panel's overall thermal performance.
Heat Transfer in PU Insulated Sandwich Panels
PU insulated sandwich panels are designed to minimize heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation. The polyurethane foam core provides excellent insulation, but the color of the exterior facing plays a crucial role in the initial heat absorption. Understanding this interplay is essential for optimizing the energy efficiency of buildings using these panels.
Color Choices and Their Impact on Thermal Performance
The color selection for PU insulated sandwich panels can have a substantial effect on a building's energy consumption and interior comfort. Let's explore how different color choices influence heat absorption and overall thermal performance.
Light-Colored Panels: The Cool Choice
Light-colored PU insulated sandwich panels, such as white, beige, or light gray, offer several advantages in terms of thermal performance:
- Higher solar reflectance, reducing heat absorption
- Lower surface temperatures, decreasing the cooling load on buildings
- Improved energy efficiency, particularly in hot climates
- Reduced risk of thermal expansion and contraction
These benefits make light-colored panels an excellent choice for buildings in warm regions or those seeking to minimize cooling costs.
Dark-Colored Panels: Balancing Aesthetics and Performance
While dark-colored PU insulated sandwich panels may offer striking aesthetic appeal, they come with some thermal considerations:
- Increased heat absorption, potentially raising interior temperatures
- Higher cooling demands in warm climates
- Potential for greater thermal stress on the panel structure
- Beneficial in cold climates where heat gain is desirable
Despite these challenges, advancements in coating technologies have led to the development of "cool" dark colors that can mitigate some of these issues.
Specialized Coatings: Enhancing Thermal Performance
The PU insulated sandwich panels factory industry has responded to the color-heat absorption challenge with innovative coating solutions:
- Solar reflective pigments that increase the albedo of darker colors
- Thermochromic coatings that change color with temperature
- Phase-change materials integrated into panel coatings
These advancements allow for greater flexibility in color selection without compromising thermal performance.
Practical Considerations for Panel Color Selection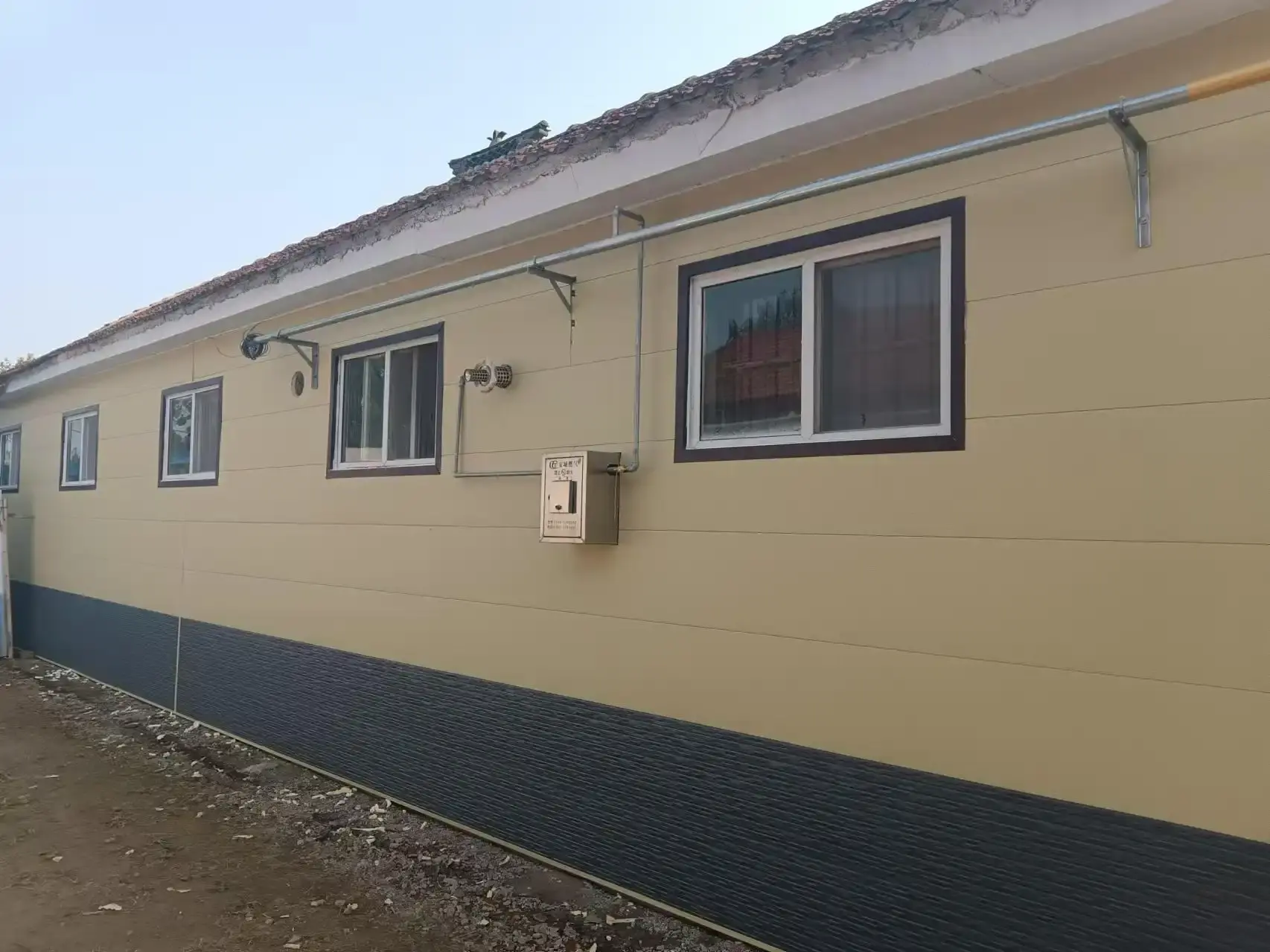
When choosing the color of PU insulated sandwich panels for a project, several factors should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Climate and Geographic Location
The local climate plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable panel color:
- Hot climates: Lighter colors are generally preferred to minimize heat gain
- Cold climates: Darker colors may be beneficial for passive solar heating
- Mixed climates: Consider seasonal variations and prioritize accordingly
Understanding the specific climatic conditions of the building site is essential for making informed color choices for PU insulated sandwich panels.
Building Orientation and Sun Exposure
The orientation of a building and its exposure to sunlight can influence the impact of panel color on heat absorption:
- South-facing walls may benefit from lighter colors to reduce heat gain
- North-facing walls have more flexibility in color choice
- East and west-facing walls may require a balanced approach
Careful consideration of these factors can help optimize the thermal performance of PU insulated sandwich panels across different building faces.
Energy Efficiency Goals and Regulations
Panel color selection should align with overall energy efficiency objectives and comply with local building codes:
- Energy Star requirements for cool roofs and walls
- LEED certification criteria for sustainable building materials
- Local energy efficiency standards and incentives
Choosing the right color for PU insulated sandwich panels can contribute significantly to meeting these goals and regulations.
Conclusion
The impact of panel color on heat absorption in PU insulated sandwich panels is a critical consideration in modern construction. While the insulating properties of these panels are primarily determined by their polyurethane core, the exterior color plays a significant role in overall thermal performance. By carefully selecting panel colors based on climate, building orientation, and energy efficiency goals, architects and builders can optimize the benefits of PU insulated sandwich panels. As the industry continues to innovate with advanced coatings and materials, the possibilities for balancing aesthetic appeal with thermal efficiency will only expand.
At Sandong Building Materials, we understand the importance of color in thermal performance. Our range of PU insulated sandwich panels offers a variety of color options to suit diverse architectural needs while maintaining excellent insulation properties. Whether you're looking for energy-efficient solutions for new construction or seeking to enhance the thermal performance of existing structures, our expert team is here to help. Contact us at info@sdqsc.com to explore how our PU insulated sandwich panels can elevate your next project.
FAQ
How significant is the impact of color on the thermal performance of PU insulated sandwich panels?
Color can significantly affect thermal performance, with lighter colors generally absorbing less heat and darker colors absorbing more. The exact impact depends on factors like climate and panel orientation.
Can I use dark-colored PU insulated sandwich panels in hot climates?
While not ideal, it's possible with advanced coatings that enhance solar reflectance. However, lighter colors are generally recommended for hot climates to minimize heat absorption.
Do specialized coatings affect the durability of PU insulated sandwich panels?
High-quality coatings can enhance durability by providing additional protection against UV radiation and weathering, potentially extending the lifespan of the panels.
References
1. Akbari, H., et al. (2008). "Cool Colors for Heat Island Mitigation." Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
2. Gentle, A.R., et al. (2011). "Optimized cool roofs: Integrating albedo and thermal emittance with R-value." Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells.
3. Pisello, A.L. (2017). "State of the art on the development of cool coatings for buildings and cities." Solar Energy.
4. Santamouris, M., et al. (2011). "Using cool paving materials to improve microclimate of urban areas – Design realization and results of the flisvos project." Building and Environment.
5. Synnefa, A., et al. (2007). "On the development, optical properties and thermal performance of cool colored coatings for the urban environment." Solar Energy.