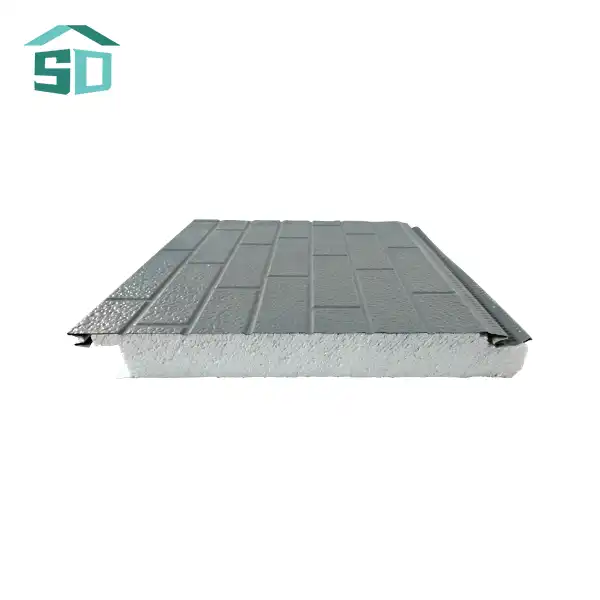
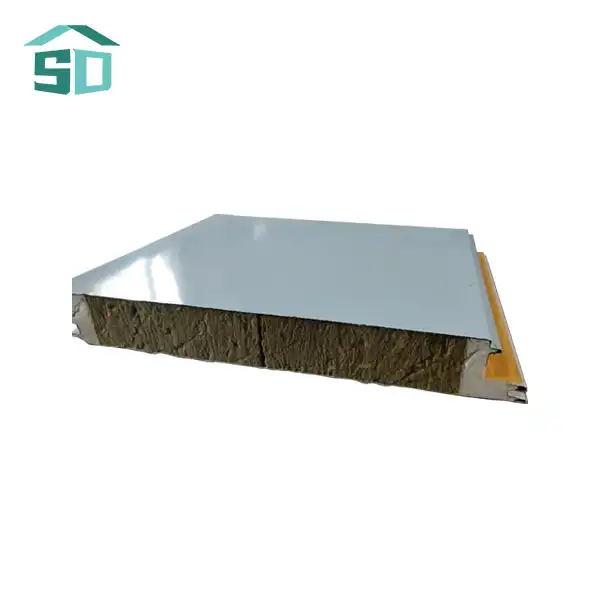
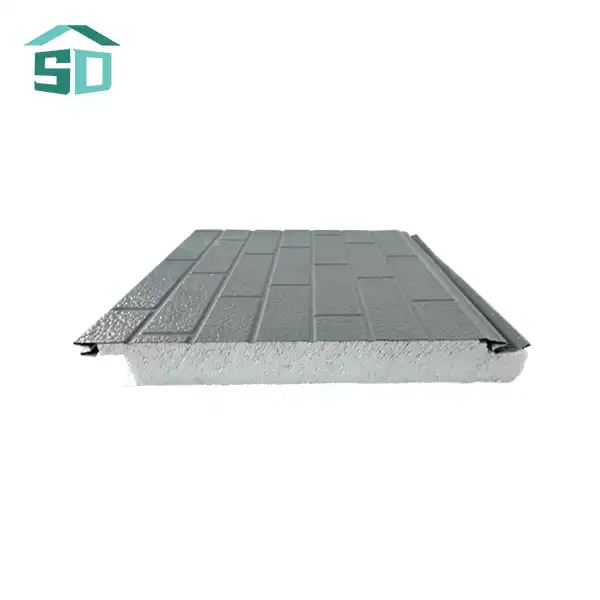
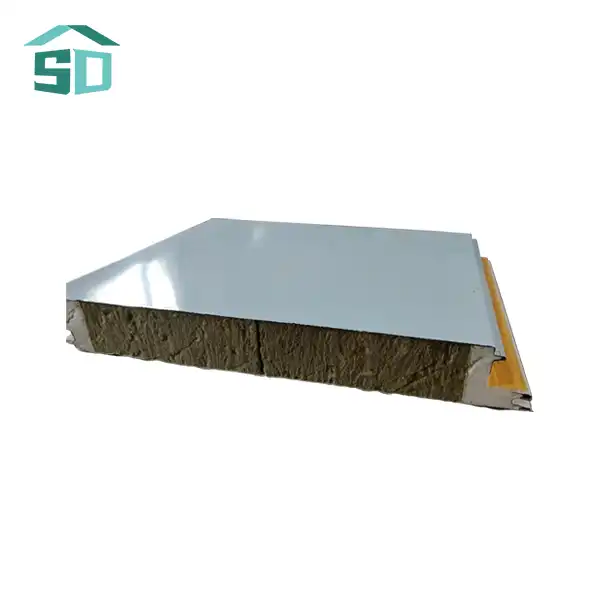
Components and Material Composition of Corrugated Sandwich Panels
Metal Facings: Steel and Aluminum Options
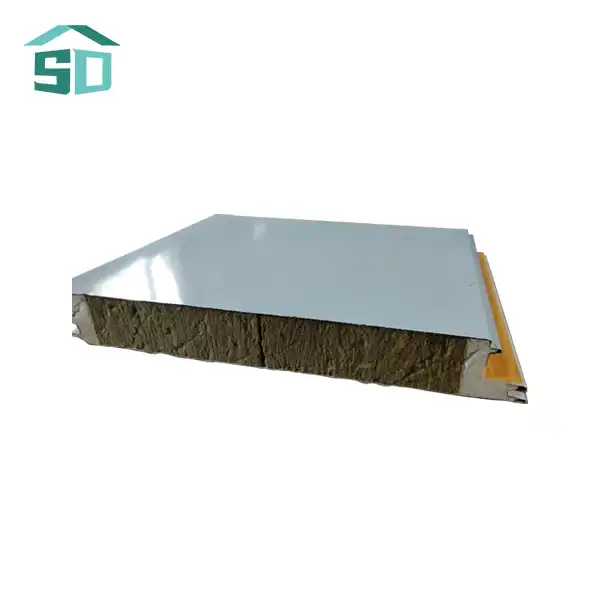
Corrugated sandwich panels rely heavily on the strength and durability of their metal facings. The two most common materials used for these facings are steel and aluminum. Each metal offers unique properties that make them suitable for different applications.
Steel facings are renowned for their exceptional strength and rigidity. They provide excellent structural support and are often chosen for larger commercial and industrial buildings. Steel-faced corrugated sandwich panels can withstand significant loads and are resistant to impact damage. Additionally, steel facings can be galvanized or coated with various finishes to enhance their corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Aluminum facings, on the other hand, offer a lightweight alternative without compromising on durability. These panels are particularly popular in applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in the transportation industry or for retrofitting existing structures. Aluminum-faced corrugated sandwich panels are naturally corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for coastal or high-humidity environments. They also provide a sleek, modern appearance that architects and designers often prefer for contemporary building projects.
Insulation Core Materials: PUR, PIR, and Mineral Wool
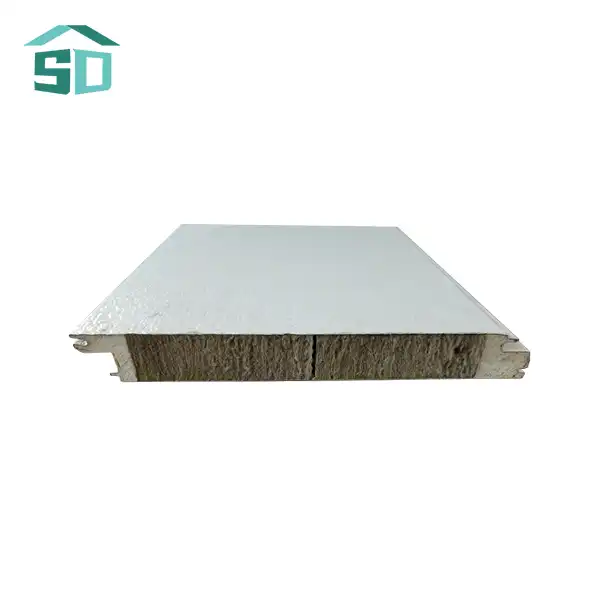
The insulation core is a critical component of corrugated sandwich panels, providing thermal efficiency and contributing to the overall structural integrity of the panel. Three primary materials are commonly used for the insulation core: polyurethane (PUR), polyisocyanurate (PIR), and mineral wool.
Polyurethane (PUR) foam is a popular choice for corrugated sandwich panel cores due to its excellent thermal insulation properties. PUR foam offers a high insulation value per inch of thickness, allowing for thinner panels without compromising on energy efficiency. It also provides good adhesion to the metal facings, ensuring the structural integrity of the panel.
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam is an advanced version of PUR foam, offering enhanced fire resistance properties. PIR-cored corrugated sandwich panels are often preferred in applications where fire safety is a primary concern. These panels maintain their excellent thermal insulation properties while providing improved fire performance.
Mineral wool, also known as rock wool, is another common insulation core material used in corrugated sandwich panels. It is made from natural rock or recycled materials and offers excellent fire resistance and sound insulation properties. Mineral wool-cored panels are often chosen for projects requiring superior acoustic performance or in areas with stringent fire safety regulations.
Protective Coatings and Finishes
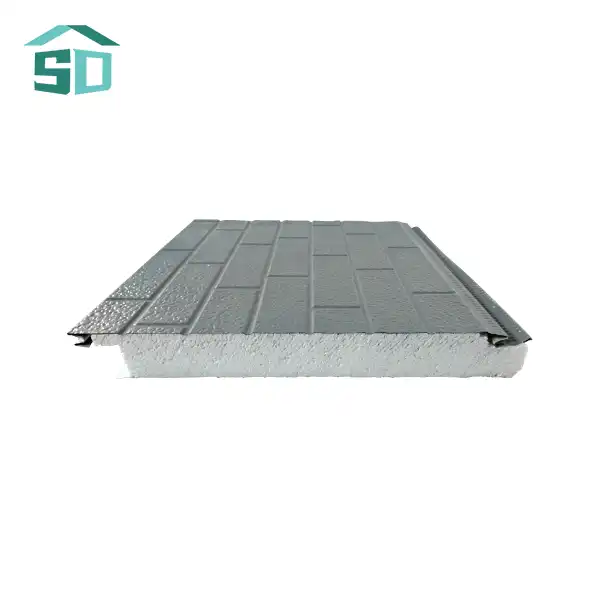
To enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of corrugated sandwich panels, various protective coatings and finishes are applied to the metal facings. These coatings not only protect the panels from environmental factors but also allow for customization to meet specific design requirements.
One of the most common protective coatings used on steel-faced corrugated sandwich panels is galvanization. This process involves applying a zinc coating to the steel, creating a barrier against corrosion and extending the lifespan of the panel. Galvanized steel panels are particularly suitable for exterior applications or in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
For enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic options, many corrugated sandwich panel manufacturers offer pre-painted steel or aluminum facings. These coatings are typically applied using a coil coating process, ensuring a uniform and durable finish. Popular coating options include polyester, PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride), and plastisol. Each coating type offers different levels of durability, color retention, and resistance to weathering.
In addition to protective coatings, corrugated sandwich panels can be finished with various textures and patterns to achieve specific architectural designs. Embossed or micro-ribbed surfaces can add visual interest and depth to the panels, while also helping to conceal minor imperfections or dents that may occur during installation or use.
Factors Influencing Material Selection for Corrugated Sandwich Panels
Environmental Considerations and Performance Requirements
When selecting materials for corrugated sandwich panels, environmental factors play a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and performance of the building envelope. The choice of materials must take into account the specific climate conditions, exposure to elements, and potential environmental hazards that the panels will face.
In coastal regions or areas with high humidity, corrosion resistance becomes a primary concern. Aluminum-faced corrugated sandwich panels or steel panels with advanced corrosion-resistant coatings are often preferred in these environments. The insulation core material should also be chosen carefully to prevent moisture absorption and maintain its thermal properties over time.
For projects in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, the thermal expansion and contraction of materials must be considered. The selected materials should have compatible coefficients of thermal expansion to prevent warping or delamination of the panels. Additionally, the insulation core material should provide consistent performance across a wide temperature range.
In areas prone to seismic activity or high wind loads, the structural performance of corrugated sandwich panels becomes paramount. Steel-faced panels with high-density insulation cores may be preferred for their superior strength and rigidity. The fastening systems and panel joints should also be designed to withstand potential movement and loads.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
The selection of materials for corrugated sandwich panels is also influenced by regulatory requirements and industry standards. Building codes and regulations vary by region and often dictate specific performance criteria that materials must meet.
Fire safety is a critical consideration in material selection, particularly for commercial and industrial buildings. Many jurisdictions require building materials to meet specific fire resistance ratings. PIR-cored corrugated sandwich panels or those with mineral wool cores are often chosen for their superior fire performance. The metal facings and coatings should also be selected to meet fire spread and smoke development requirements.
Energy efficiency standards and green building certifications also impact material choices for corrugated sandwich panels. The overall thermal performance of the panel, including the insulation core and any thermal breaks, must meet or exceed local energy codes. Additionally, materials with recycled content or those that contribute to sustainable building practices may be preferred for projects seeking green building certifications.
In the food processing and pharmaceutical industries, corrugated sandwich panels must often meet strict hygiene standards. Panels with smooth, non-porous surfaces and antimicrobial coatings may be required to prevent the growth and spread of bacteria. The materials should also be resistant to cleaning chemicals and able to withstand frequent washing.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
While performance and regulatory compliance are critical factors in material selection, cost-effectiveness and long-term value also play significant roles in the decision-making process for corrugated sandwich panels.
The initial cost of materials is an important consideration, but it should be balanced against the long-term performance and maintenance requirements of the panels. For example, while aluminum-faced panels may have a higher upfront cost compared to steel, their corrosion resistance and lighter weight could result in lower maintenance costs and reduced structural requirements over the life of the building.
The energy efficiency provided by the insulation core material can significantly impact the long-term operational costs of a building. Higher-performing insulation materials may command a premium price but can lead to substantial energy savings over time, particularly in regions with extreme climates or high energy costs.
The durability and expected lifespan of the materials should also be factored into the cost-effectiveness equation. High-quality coatings and finishes may increase the initial cost of corrugated sandwich panels but can extend their service life and reduce the need for replacement or refurbishment.
Innovations and Future Trends in Corrugated Sandwich Panel Materials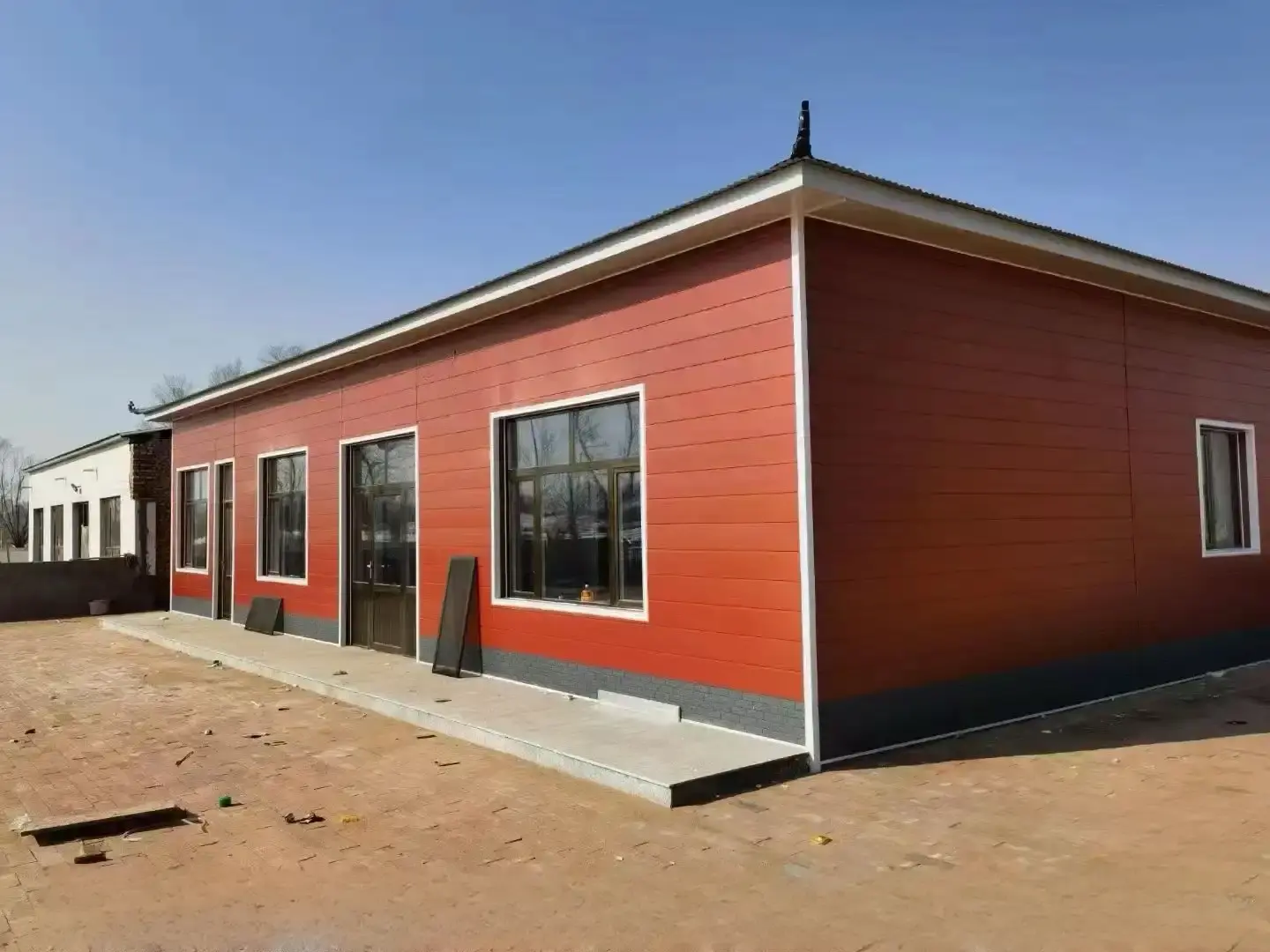
Advanced Composite Materials and Nanotechnology
The field of corrugated sandwich panel manufacturing is continuously evolving, with new materials and technologies emerging to enhance performance and sustainability. Advanced composite materials are at the forefront of these innovations, offering improved strength-to-weight ratios and unique properties that traditional materials cannot match.
Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) are being explored as alternatives to metal facings in corrugated sandwich panels. These materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and the ability to be molded into complex shapes. FRP-faced panels can be particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical or where electromagnetic transparency is required, such as in radar installations or telecommunications structures.
Nanotechnology is also making its way into corrugated sandwich panel materials. Nano-enhanced coatings can provide superior weather resistance, self-cleaning properties, and even air-purifying capabilities. These coatings can extend the lifespan of panels and reduce maintenance requirements, making them particularly attractive for high-rise buildings or structures in polluted urban environments.
In the realm of insulation core materials, aerogels are showing promise as ultra-high-performance insulators. These materials offer exceptional thermal insulation properties with minimal thickness, potentially allowing for slimmer corrugated sandwich panels without compromising on energy efficiency. While currently cost-prohibitive for widespread use, ongoing research and development may make aerogel-cored panels more economically viable in the future.
Sustainable and Recyclable Materials
As the construction industry increasingly focuses on sustainability, corrugated sandwich panel manufacturers are exploring more environmentally friendly material options. Bio-based insulation materials, such as those derived from soy or hemp, are being developed as alternatives to petroleum-based foams. These materials offer comparable insulation properties while reducing the carbon footprint of panel production.
Recycled content is becoming a key consideration in material selection for corrugated sandwich panels. Steel and aluminum facings with high recycled content are becoming more readily available, reducing the demand for virgin materials. Similarly, insulation cores made from recycled plastics or industrial waste products are being developed to create more circular material streams.
End-of-life considerations are also driving innovation in panel design. Some manufacturers are exploring modular panel systems that can be easily disassembled and recycled at the end of their useful life. This approach not only reduces waste but also allows for easier upgrades and modifications to buildings over time.
Smart Materials and Integrated Technologies
The integration of smart technologies into corrugated sandwich panels is an emerging trend that promises to revolutionize building envelopes. Phase change materials (PCMs) incorporated into the insulation core can help regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and releasing heat as needed, potentially reducing HVAC energy consumption.
Photovoltaic cells integrated directly into the panel facings are another exciting development. These "solar sandwich panels" can generate electricity while still providing the structural and insulating properties of traditional corrugated sandwich panels. This technology is particularly promising for large commercial and industrial buildings with extensive facade areas.
Sensors embedded within corrugated sandwich panels can provide real-time data on structural health, thermal performance, and environmental conditions. This information can be used for predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and improved building management. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, these smart panels could become an integral part of intelligent building systems.
Self-healing materials are also being explored for use in corrugated sandwich panels. These materials can automatically repair minor damage, such as scratches or small punctures, potentially extending the lifespan of panels and reducing maintenance costs. While still in the early stages of development, self-healing coatings and insulation materials could significantly enhance the durability of corrugated sandwich panels in the future.
Conclusion
Corrugated sandwich panels have become an integral part of modern construction, offering a combination of structural strength, thermal efficiency, and aesthetic versatility. The common materials used in these panels, including steel and aluminum facings, insulation cores like PUR, PIR, and mineral wool, and various protective coatings, provide a range of options to meet diverse project requirements. As the industry continues to innovate, we can expect to see even more advanced materials and technologies incorporated into corrugated sandwich panels, further enhancing their performance and sustainability.
For those seeking high-quality corrugated sandwich panels and expert guidance on material selection, Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. offers a comprehensive range of exterior cladding and facade solutions. To learn more about our products and how they can benefit your next project, please contact us at info@sdqsc.com.
FAQs
What is the typical lifespan of a corrugated sandwich panel?
The lifespan of a corrugated sandwich panel can vary depending on the materials used and environmental conditions, but high-quality panels can last 30-50 years or more with proper maintenance.
Are corrugated sandwich panels fire-resistant?
Many corrugated sandwich panels offer fire resistance, especially those with PIR or mineral wool cores. However, the level of fire resistance can vary, so it's important to choose panels that meet local building codes and fire safety requirements.
Can corrugated sandwich panels be recycled?
Yes, many components of corrugated sandwich panels can be recycled, particularly the metal facings. Some manufacturers are also developing fully recyclable panel systems to improve sustainability.
References
1. Davies, J.M. (2001). Lightweight sandwich construction. John Wiley & Sons.
2. Zenkert, D. (1997). The handbook of sandwich construction. Engineering Materials Advisory Services Ltd.
3. Birman, V., & Kardomateas, G.A. (2018). Review of current trends in research and applications of sandwich structures. Composites Part B: Engineering, 142, 221-240.
4. Pflug, J., Vangrimde, B., & Verpoest, I. (2003). Material efficiency and cost effectiveness of sandwich materials. Proceedings of the SAMPE Europe Conference, Paris, France.
5. Ashby, M.F. (2011). Materials selection in mechanical design. Butterworth-Heinemann.