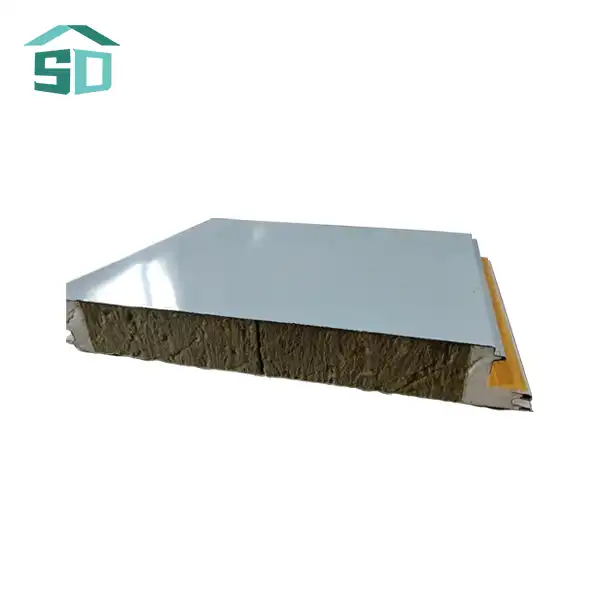
Common Types of Metal Sandwich Panel Failures
Metal sandwich panels are engineered to provide superior insulation, strength, and versatility in construction. However, several factors can lead to their failure, compromising the integrity and efficiency of the building envelope. Let's delve into the most prevalent types of failures associated with metal sandwich panels:
Delamination: The Silent Destroyer
Delamination occurs when the layers of a metal sandwich panel separate, typically due to adhesive failure or moisture infiltration. This issue can severely impact the panel's structural integrity and insulation properties. Signs of delamination include visible separation between the metal face and the core material, bubbling on the surface, or a hollow sound when tapped.
To mitigate delamination risks, it's crucial to:
- Ensure proper storage and handling of panels before installation
- Use high-quality adhesives recommended by the manufacturer
- Implement effective moisture barriers during installation
- Regularly inspect panels for early signs of separation
Corrosion: The Gradual Degradation
Despite their corrosion-resistant design, metal sandwich panels can still fall victim to this electrochemical process under certain conditions. Corrosion not only affects the aesthetic appeal but can also compromise the panel's structural integrity. Factors contributing to corrosion include:
- Exposure to harsh environmental conditions (e.g., coastal areas with high salt content)
- Chemical exposure in industrial settings
- Improper sealing at joints and edges
- Damage to protective coatings
To combat corrosion, consider:
- Selecting panels with enhanced corrosion-resistant coatings
- Implementing regular maintenance and cleaning routines
- Addressing any damage to the panel surface promptly
- Ensuring proper drainage and ventilation in the building design
Thermal Bowing: The Shape-Shifting Challenge
Thermal bowing occurs when temperature differences between the exterior and interior faces of the panel cause it to curve or warp. This phenomenon can lead to aesthetic issues, compromised insulation, and potential structural problems. Factors influencing thermal bowing include:
- Panel color (darker colors absorb more heat)
- Panel length and thickness
- Installation method and fastening systems
- Extreme temperature fluctuations
To minimize thermal bowing:
- Opt for lighter-colored panels in areas with high solar exposure
- Consider using shorter panel lengths or incorporating expansion joints
- Ensure proper installation techniques that allow for thermal movement
- Implement adequate insulation and ventilation in the building design
Preventing Metal Sandwich Panel Failures
While metal sandwich panels offer numerous benefits, preventing failures is key to maximizing their performance and longevity. By implementing proactive measures and adhering to best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of panel failures and ensure the durability of your structure.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
The foundation of reliable metal sandwich panels begins at the manufacturing stage. Reputable manufacturers, like Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., employ rigorous quality control measures to ensure the production of high-performance panels. These measures include:
- Comprehensive testing of raw materials (steel coils, aluminum foil, insulation cores)
- Strict monitoring of panel thickness, paint film thickness, and mechanical strength
- Flame retardancy tests to meet international fire safety standards
- Visual inspections for product appearance and consistency
By choosing panels from manufacturers with stringent quality control processes, you significantly reduce the risk of inherent defects that could lead to failures.
Proper Installation Techniques
Even the highest quality metal sandwich panels can fail if not installed correctly. Proper installation is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of the panels. Key considerations include:
- Thorough surface preparation before panel installation
- Accurate measurements and precise cutting of panels when necessary
- Correct use of fasteners and adhesives as recommended by the manufacturer
- Proper sealing of joints and edges to prevent moisture infiltration
- Allowing for thermal expansion and contraction in the installation design
Professional installation by experienced contractors can significantly reduce the risk of failures associated with improper mounting or sealing.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Implementing a routine maintenance schedule is essential for identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into significant failures. Regular maintenance should include:
- Visual inspections for signs of damage, corrosion, or delamination
- Cleaning of panels to remove dirt, debris, and potential corrosive substances
- Checking and resealing of joints and fasteners as needed
- Prompt repair of any identified damage or wear
By staying vigilant and addressing minor issues promptly, you can prevent many common failures and extend the lifespan of your metal sandwich panels.
Innovations in Metal Sandwich Panel Technology
As the construction industry evolves, so does the technology behind metal sandwich panels. Manufacturers and researchers are continuously working to enhance the performance and durability of these versatile building materials. Let's explore some of the cutting-edge innovations aimed at mitigating common failures and improving overall panel performance.
Advanced Coating Technologies
One of the most significant advancements in metal sandwich panel technology is the development of superior coating systems. These innovative coatings offer enhanced protection against corrosion, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. Some notable developments include:
- Nanotechnology-based coatings that provide self-cleaning and anti-microbial properties
- Multi-layer coating systems that offer improved resistance to scratches and impacts
- Smart coatings that can change color or opacity in response to environmental conditions
- Eco-friendly, low-VOC coatings that maintain high performance while reducing environmental impact
These advanced coatings not only extend the lifespan of metal sandwich panels but also contribute to improved energy efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements.
Improved Core Materials
The core of a metal sandwich panel plays a crucial role in its overall performance. Recent innovations in core materials have led to significant improvements in panel strength, insulation properties, and fire resistance. Some noteworthy advancements include:
- Hybrid core materials that combine the benefits of different insulation types
- Nano-enhanced foam cores with improved thermal performance and structural integrity
- Bio-based core materials that offer sustainable alternatives without compromising performance
- Phase-change materials (PCMs) integrated into cores for enhanced thermal regulation
These innovative core materials contribute to the creation of metal sandwich panels that are not only more resistant to failures but also more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Smart Panel Systems
The integration of smart technologies into metal sandwich panels represents a significant leap forward in building envelope design. These intelligent systems can help prevent failures by providing real-time monitoring and early detection of potential issues. Features of smart panel systems include:
- Embedded sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, and structural integrity
- IoT connectivity for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance
- Self-healing capabilities that can address minor damage automatically
- Integration with building management systems for optimized performance
By leveraging these smart technologies, building owners and managers can proactively address potential failures before they become significant problems, ensuring the longevity and efficiency of their structures.
Conclusion
Understanding the potential failures of metal sandwich panels is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of buildings that utilize these versatile materials. By being aware of common issues like delamination, corrosion, and thermal bowing, and implementing preventive measures, architects, builders, and property owners can maximize the benefits of metal sandwich panels while minimizing risks.
As technology continues to advance, the future of metal sandwich panels looks promising, with innovations addressing current limitations and enhancing overall performance. By staying informed about these developments and choosing high-quality products from reputable manufacturers, you can ensure that your building projects benefit from the best that metal sandwich panel technology has to offer.
For more information on cutting-edge metal sandwich panels and expert advice on their application in your next project, don't hesitate to contact us at info@sdqsc.com. Our team at Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd. is dedicated to providing you with the highest quality exterior cladding and facade solutions, backed by our commitment to innovation and excellence in the building materials industry.