The Science Behind Insulated Thermal Wall Panels
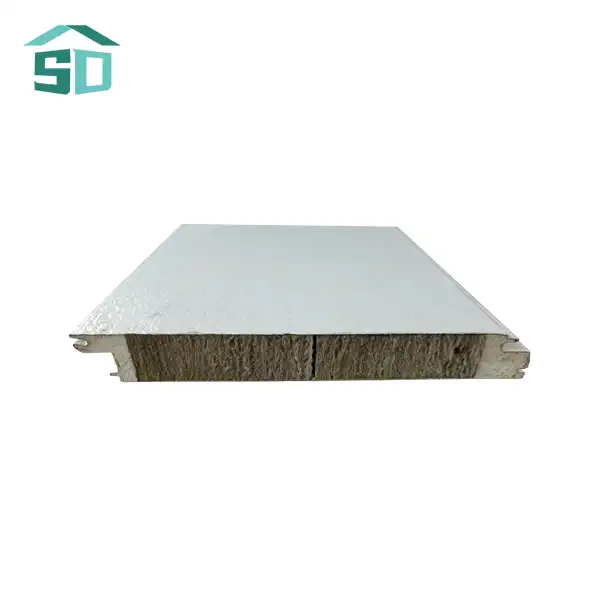
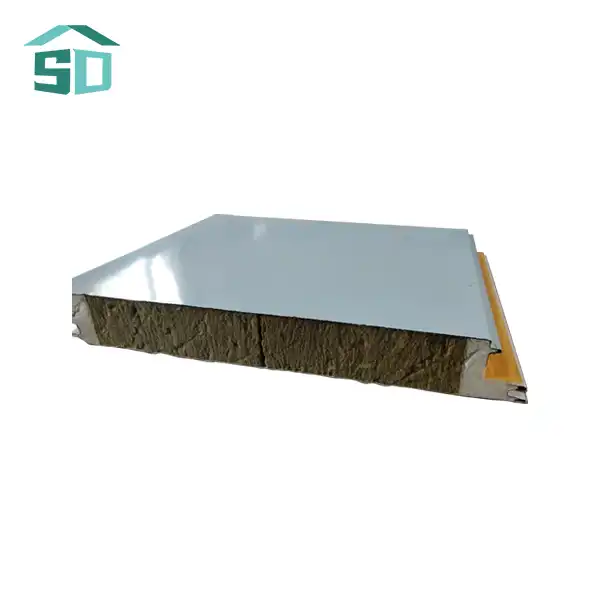
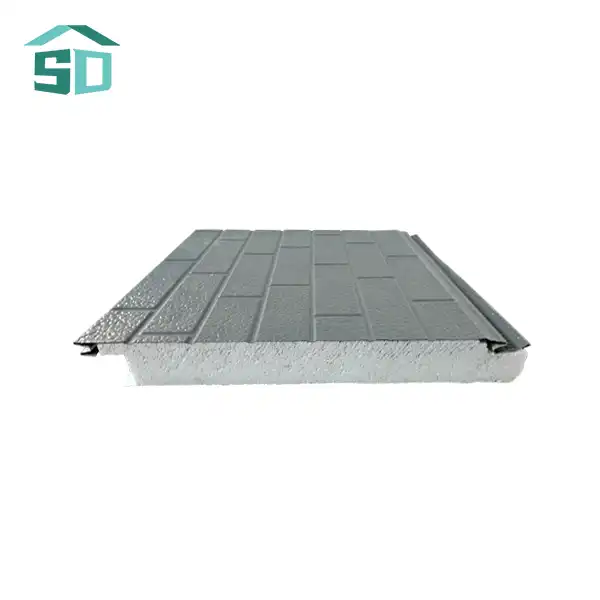
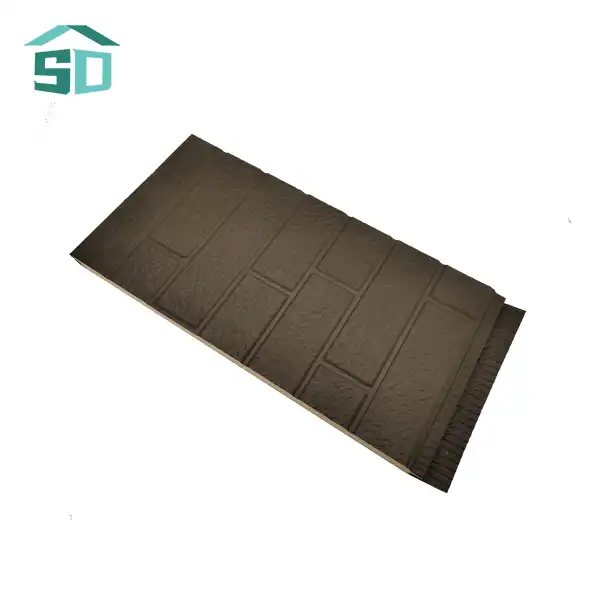
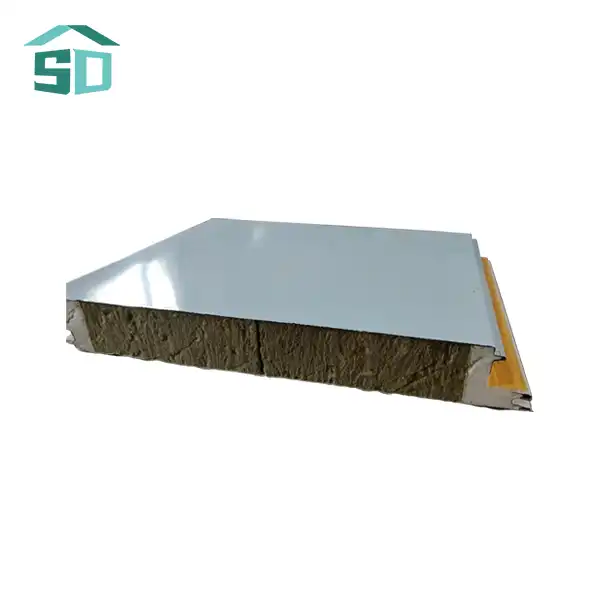
Insulated thermal wall panels are engineered to maximize energy efficiency through their unique composition and design. These panels typically consist of a high-performance insulation core sandwiched between two structural facings. The insulation core, often made of materials like polyurethane, polystyrene, rock wool, or glass wool, provides excellent thermal resistance. This core is crucial in preventing heat flow through the walls, effectively maintaining desired indoor temperatures with minimal energy input.
The R-value, a measure of thermal resistance, is significantly higher in insulated thermal wall panels compared to traditional building materials. This enhanced R-value translates to better insulation performance, reducing the workload on HVAC systems and consequently lowering energy consumption. The structural facings, which can be made of aluminum, steel, stainless steel, or copper, not only provide durability but also contribute to the overall thermal performance of the panel.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
The manufacturing process of insulated thermal wall panels involves cutting-edge technology to ensure consistent quality and performance. Advanced production lines equipped with precision machinery allow for the creation of panels with uniform thickness and density. This consistency is vital for maintaining the panels' insulation properties across the entire surface area, eliminating weak points that could compromise energy efficiency.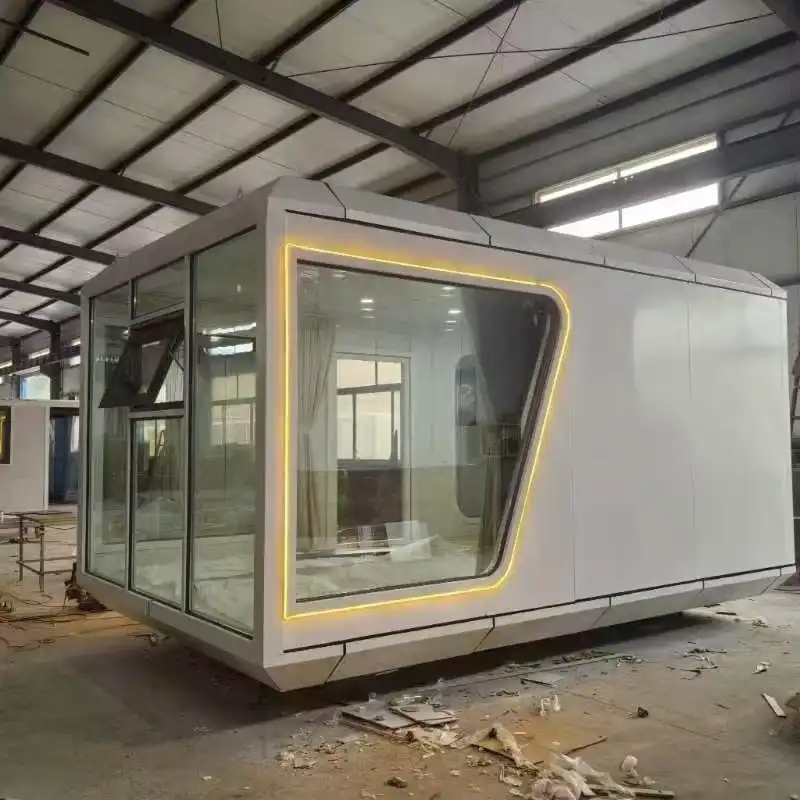
Thermal Bridging Prevention
One of the key advantages of insulated thermal wall panels is their ability to minimize thermal bridging. Thermal bridges are areas in the building envelope where heat can easily transfer, reducing overall insulation effectiveness. The continuous insulation provided by these panels effectively eliminates most thermal bridges, resulting in a more energy-efficient building envelope.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The use of insulated thermal wall panels has a profound impact on a building's environmental footprint. By significantly reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling, these panels directly contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production. This reduction in carbon footprint aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and meets increasingly stringent building energy codes and standards.
Moreover, the longevity and durability of insulated thermal wall panels contribute to their sustainability. With proper installation and maintenance, these panels can maintain their performance for decades, reducing the need for replacement and minimizing construction waste. Many manufacturers also prioritize the use of recyclable materials in panel production, further enhancing their eco-friendly profile.
Life Cycle Assessment
A comprehensive life cycle assessment of insulated thermal wall panels reveals their long-term environmental benefits. While the production of these panels does require energy and resources, the energy savings over the lifespan of a building far outweigh the initial environmental cost. This positive net impact makes insulated thermal wall panels a sustainable choice for modern construction projects.
Contribution to Green Building Certifications
The use of insulated thermal wall panels can significantly contribute to achieving green building certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). These panels help meet criteria for energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and sustainable materials, potentially earning projects valuable points towards certification.
Versatility and Aesthetic Appeal
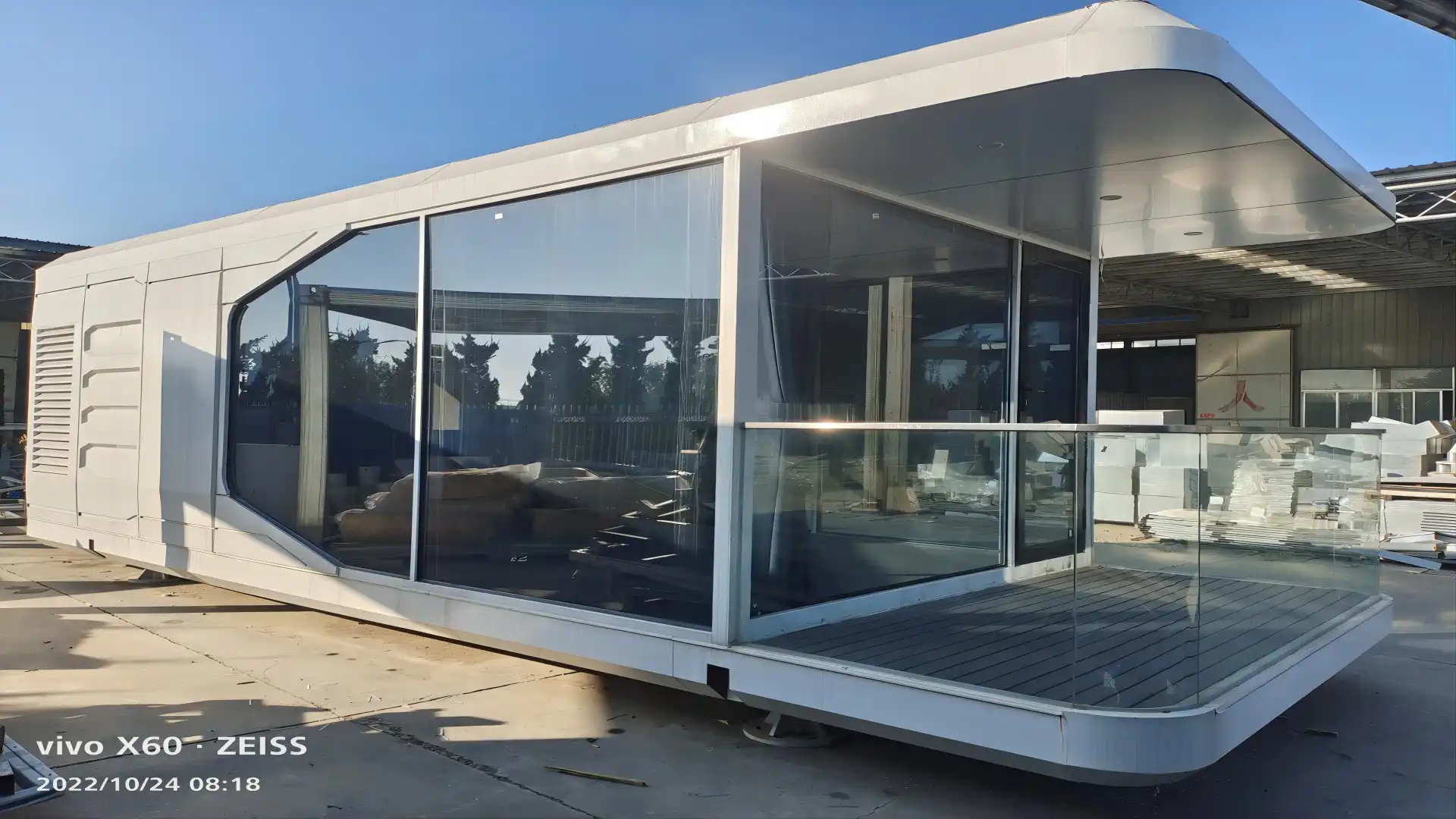
Insulated thermal wall panels are not just about functionality; they also offer remarkable versatility in design and aesthetics. Available in a wide range of colors, finishes, and textures, these panels can complement various architectural styles, from sleek modern designs to more traditional facades. This versatility allows architects and designers to achieve their desired aesthetic without compromising on energy efficiency.
The panels' customizable nature extends beyond appearance. They are available in various thicknesses, typically ranging from 50mm to 100mm, with custom options available to meet specific project requirements. This flexibility in sizing ensures that insulated thermal wall panels can be adapted to diverse building types and climatic conditions, optimizing performance for each unique application.
Integration with Building Systems
Insulated thermal wall panels seamlessly integrate with other building systems, enhancing overall performance. Their compatibility with various fastening systems and accessories allows for easy installation of exterior claddings, interior finishes, and building services. This integration capability simplifies the construction process, reducing on-site labor and potential errors.
Fire Safety and Weather Resistance
Beyond their thermal properties, insulated thermal wall panels offer additional benefits that contribute to building safety and durability. Many panels are manufactured to meet stringent fire safety standards, with fire ratings of Class A or B1, providing an added layer of protection to the building envelope. Furthermore, their weather-resistant properties, including UV and corrosion resistance, ensure long-lasting performance in various environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Insulated thermal wall panels represent a significant advancement in building techn logy, offering a powerful solution for improving energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprints. Their ability to enhance R-value while providing versatile design options makes them an attractive choice for modern construction projects. As the building industry continues to prioritize sustainability and energy conservation, these panels stand out as a key component in creating high-performance, environmentally responsible buildings. The long-term benefits of reduced energy consumption, lower maintenance costs, and improved occupant comfort solidify the position of insulated thermal wall panels as a smart investment in the future of construction.
At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we are committed to providing top-quality insulated thermal wall panels that meet the evolving needs of the construction industry. Our products are designed to deliver exceptional thermal performance, durability, and aesthetic versatility. To learn more about how our insulated thermal wall panels can benefit your next project, please contact us at info@sdqsc.com.
FAQ
What are the main advantages of using insulated thermal wall panels?
Insulated thermal wall panels offer superior energy efficiency, improved R-value, reduced carbon footprint, versatile design options, and simplified installation processes.
How do insulated thermal wall panels contribute to sustainability?
These panels reduce energy consumption, minimize thermal bridging, and often use recyclable materials, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions and less construction waste.
Are insulated thermal wall panels suitable for all types of buildings?
Yes, they are versatile and can be used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, as well as for renovations and new constructions.
References
1.U.S. Department of Energy. (2022). "Insulation Materials." Energy Saver.
2.American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE). (2021). "ASHRAE Handbook - Fundamentals."
3.U.S. Green Building Council. (2023). "LEED rating system."
4.National Institute of Building Sciences. (2022). "Whole Building Design Guide: Building Envelope Design Guide."