Grasping PU Insulated Sandwich Panels and Their Thermal Properties
The Composition and Structure of PU Insulated Sandwich Panels
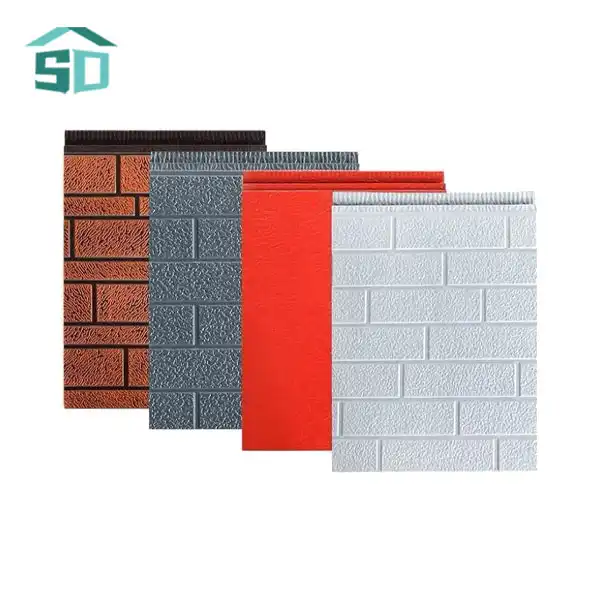
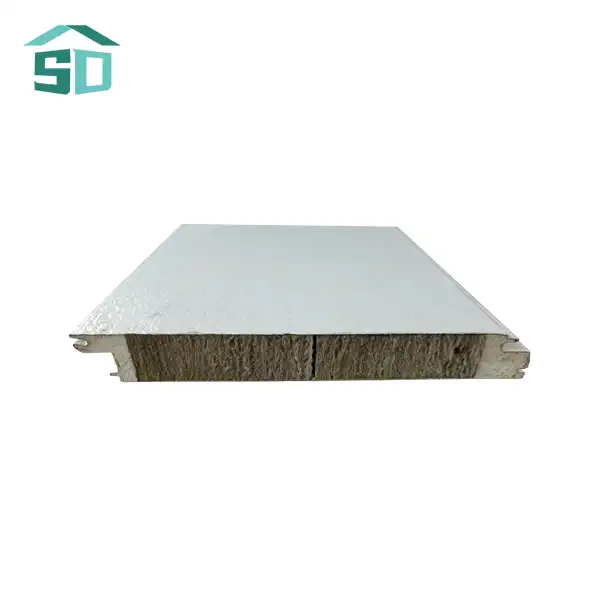
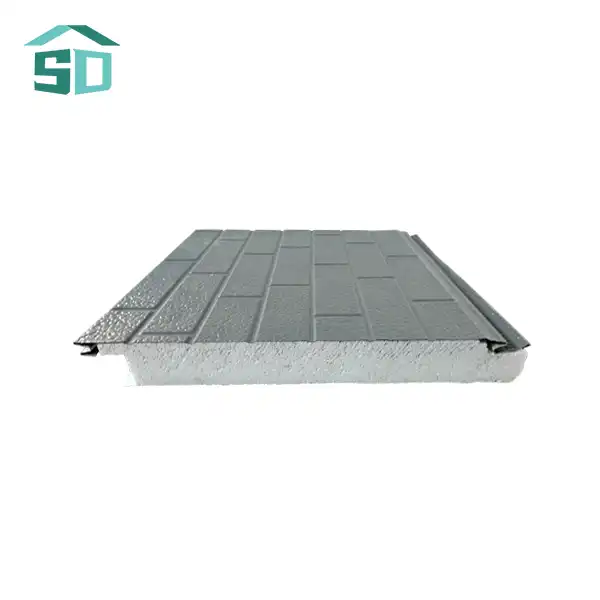
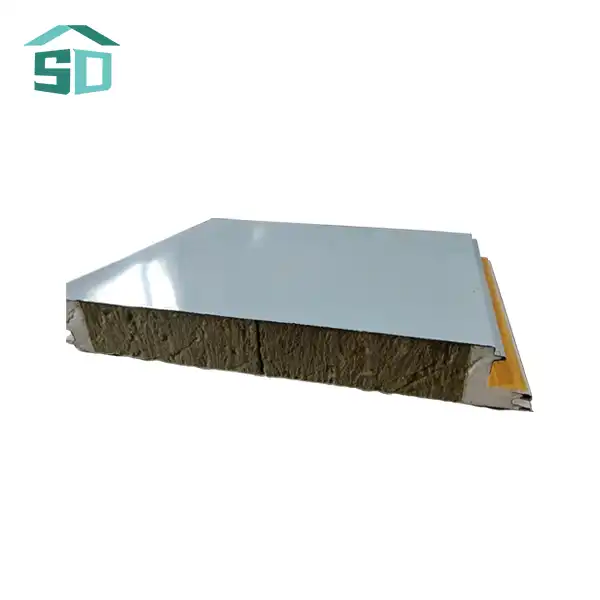
PU insulated sandwich panels are advanced building materials consisting of three primary layers. The core is made of rigid polyurethane foam, renowned for its exceptional insulating properties. This core is sandwiched between two metal facings, typically made of steel or aluminum. The unique composition of these panels contributes to their superior thermal performance and structural integrity.
The polyurethane core in PU insulated sandwich panels is characterized by its closed-cell structure, which significantly impedes heat transfer. This structure creates tiny air pockets that act as barriers to thermal conductivity, enhancing the panel's insulation capabilities. The metal facings not only provide strength and durability but also contribute to the panel's overall thermal resistance by reflecting radiant heat.
Thermal Conductivity and R-Value of PU Insulated Sandwich Panels
The thermal performance of PU insulated sandwich panels is primarily measured by their thermal conductivity (λ-value) and thermal resistance (R-value). The thermal conductivity of these panels is impressively low, typically around 0.023 W/mK, which is superior to many traditional insulation materials. This low conductivity translates to high R-values, indicating excellent insulation properties.
The R-value of PU insulated sandwich panels increases with thickness. For instance, a 50mm thick panel might have an R-value of about 2.17 m²K/W, while a 100mm panel could reach 4.35 m²K/W or higher. This scalability allows builders and architects to select the optimal thickness based on specific climate requirements and energy efficiency goals.
Factors Affecting the Insulation Performance of PU Panels
Several factors influence the insulation performance of PU insulated sandwich panels. The density of the polyurethane foam is a critical factor; higher density generally correlates with better insulation properties. The quality of the manufacturing process, including the bonding between the core and facings, can also impact thermal performance.
Environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature can affect the long-term performance of PU insulated sandwich panels. High-quality panels are designed to maintain their insulation properties over time, resisting degradation from moisture and temperature fluctuations. The installation method also plays a role, as proper sealing and joining of panels are essential to prevent thermal bridges and maintain overall insulation efficiency.
Climate Zone Classification and Its Impact on Insulation Requirements
Overview of Global Climate Zones
Climate zones are geographical areas characterized by distinct weather patterns, temperature ranges, and precipitation levels. These zones are typically classified based on factors such as average annual temperature, humidity, and seasonal variations. Common classifications include tropical, subtropical, temperate, continental, polar, and arid zones.
Each climate zone presents unique challenges for building insulation. Tropical zones, for instance, require insulation that can effectively manage high heat and humidity, while polar regions demand materials that can withstand extreme cold and provide maximum thermal retention. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for determining the optimal thickness of PU insulated sandwich panels for a specific location.
Insulation Needs Across Different Climate Zones
The insulation requirements vary significantly across climate zones. In hot climates, the primary goal is to keep heat out and maintain a cool interior. This often involves reflecting solar radiation and minimizing heat gain. PU insulated sandwich panels in these regions need to balance thermal insulation with heat reflection properties.
Cold climates, conversely, focus on retaining interior heat and preventing heat loss to the exterior. In these areas, thicker PU insulated sandwich panels are often necessary to achieve higher R-values and provide adequate thermal protection against harsh winter conditions. Temperate zones require a more balanced approach, with insulation that can effectively manage both heating and cooling needs throughout the year.
Regulatory Standards for Insulation in Various Regions
Insulation standards and building codes vary widely across different countries and regions. These regulations often specify minimum R-values or U-values (thermal transmittance) for building envelopes, including walls and roofs. For instance, in the United States, the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) provides guidelines for insulation requirements based on climate zones.
In Europe, the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) sets standards for energy efficiency in buildings, including insulation requirements. These standards often influence the choice of PU insulated sandwich panels and their thicknesses. PU insulated sandwich panels suppliers must ensure their products meet or exceed these regulatory requirements while offering solutions that are tailored to specific regional needs.
Determining Optimal PU Panel Thickness for Specific Climate Conditions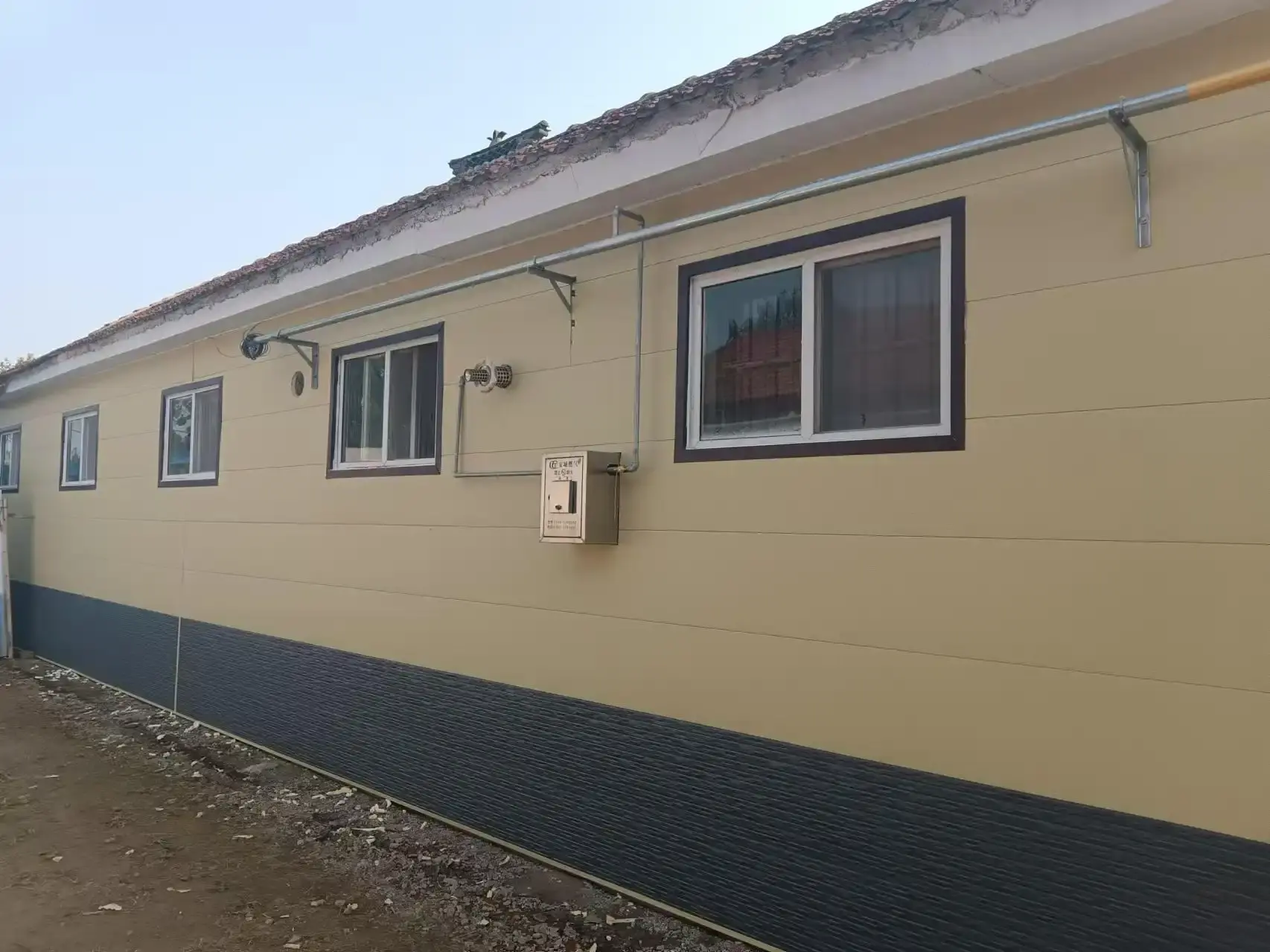
Calculating Required R-Values for Different Climates
Determining the optimal thickness of PU insulated sandwich panels begins with calculating the required R-value for a specific climate. This calculation takes into account factors such as average annual temperature, heating and cooling degree days, and desired indoor temperature. For example, a building in a cold climate might require an R-value of 20 or higher for walls, while a structure in a moderate climate might suffice with an R-value of 13-15.
To calculate the necessary panel thickness, the required R-value is divided by the R-value per inch of the PU insulated sandwich panel. For instance, if a panel provides an R-value of 6.5 per inch and the required R-value is 19.5, a 3-inch (approximately 75mm) thick panel would be suitable. This calculation ensures that the chosen panel thickness meets the specific insulation needs of the climate zone.
Recommended PU Panel Thicknesses for Major Climate Zones
Based on extensive research and practical applications, PU insulated sandwich panels suppliers typically recommend the following thicknesses for major climate zones:
- Hot-Humid Climates: 50-75mm panels for effective heat reflection and insulation
- Hot-Dry Climates: 50-100mm panels to manage extreme temperature fluctuations
- Temperate Climates: 75-100mm panels for balanced year-round performance
- Cold Climates: 100-150mm panels for maximum thermal retention
- Extreme Cold Climates: 150mm or thicker panels for superior insulation against severe cold
These recommendations serve as general guidelines and may be adjusted based on specific building requirements, local regulations, and energy efficiency goals.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of PU Panels in Various Climates
Numerous case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of properly sized PU insulated sandwich panels in different climates. For instance, a commercial building in Dubai utilized 75mm panels with specialized coatings to reflect solar radiation and maintain a cool interior despite extreme heat. The building reported a 30% reduction in cooling costs compared to conventional insulation methods.
In a contrasting example, a residential complex in Norway employed 150mm PU insulated sandwich panels for its walls and roof. This choice resulted in exceptional thermal performance, with homeowners reporting consistent indoor temperatures and significant reductions in heating expenses, even during harsh winter months. These case studies highlight the versatility and efficiency of PU insulated sandwich panels when properly matched to specific climate conditions.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal thickness for PU insulated sandwich panels is a critical decision that significantly impacts a building's energy efficiency and comfort. By considering climate zones, local regulations, and specific insulation requirements, builders and architects can make informed choices that maximize the benefits of these versatile panels. The adaptability of PU insulated sandwich panels across various climates showcases their effectiveness as a modern insulation solution, capable of meeting diverse environmental challenges while providing excellent thermal performance and structural integrity.
At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we understand the importance of choosing the right PU insulated sandwich panels for your specific climate needs. Our range of high-quality panels, available in various thicknesses and configurations, is designed to meet the most demanding insulation requirements across all climate zones. Whether you're building in a tropical paradise or a frigid tundra, our expert team is ready to assist you in selecting the perfect PU insulated sandwich panels for your project. For personalized advice and to explore our comprehensive range of insulation solutions, don't hesitate to contact us at info@sdqsc.com.
FAQs
What is the minimum thickness for PU insulated sandwich panels?
The minimum thickness typically starts at 30mm, but 50mm is more common for effective insulation.
Can PU insulated sandwich panels be used in all climate zones?
Yes, these panels are versatile and can be adapted for use in all climate zones by adjusting thickness and specifications.
How long do PU insulated sandwich panels last?
With proper installation and maintenance, these panels can last 30-50 years or more.
Are thicker PU panels always better for insulation?
While thicker panels generally provide better insulation, the optimal thickness depends on specific climate needs and building requirements.
Can PU insulated sandwich panels help reduce energy costs?
Yes, properly selected and installed panels can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs by improving energy efficiency.
References
1. International Energy Conservation Code (IECC). (2021). International Code Council.
2. Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD). (2018). European Commission.
3. Polyurethane Foam Association. (2022). "Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency of Rigid Polyurethane Foam."
4. ASHRAE. (2021). "ASHRAE Handbook - Fundamentals." American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
5. U.S. Department of Energy. (2023). "Insulation." Energy Saver.