Understanding the Science Behind Lightweight Insulation Board
Thermal Conductivity and R-Value
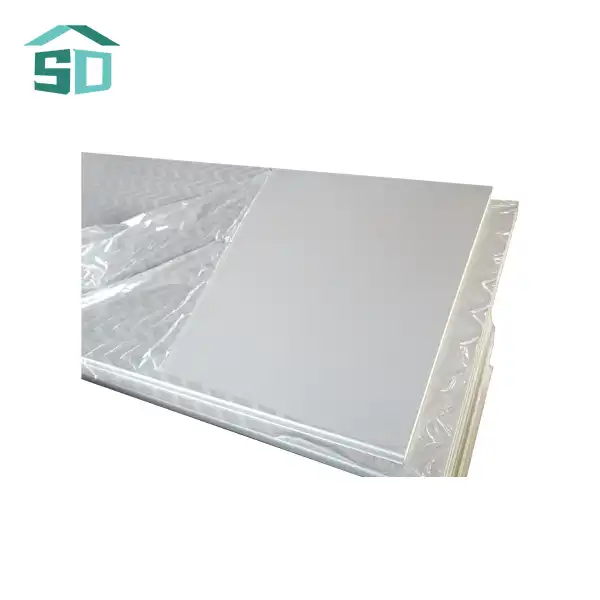
The effectiveness of Lightweight Insulation Board in protecting against heat loss is rooted in its low thermal conductivity. This property, often expressed as a K-value or λ-value, measures the material's ability to conduct heat. The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the insulation performance. Lightweight Insulation Board typically boasts a thermal conductivity ranging from 0.020 to 0.040 W/mK, depending on the specific composition and manufacturing process.
Closely related to thermal conductivity is the R-value, which quantifies the thermal resistance of the insulation material. The R-value is calculated by dividing the thickness of the material by its thermal conductivity. Lightweight Insulation Board offers impressive R-values, often exceeding 3.5 per inch of thickness. This high R-value translates to exceptional insulating capabilities, ensuring that heat remains where it's intended – inside during winter and outside during summer.
Density and Porosity
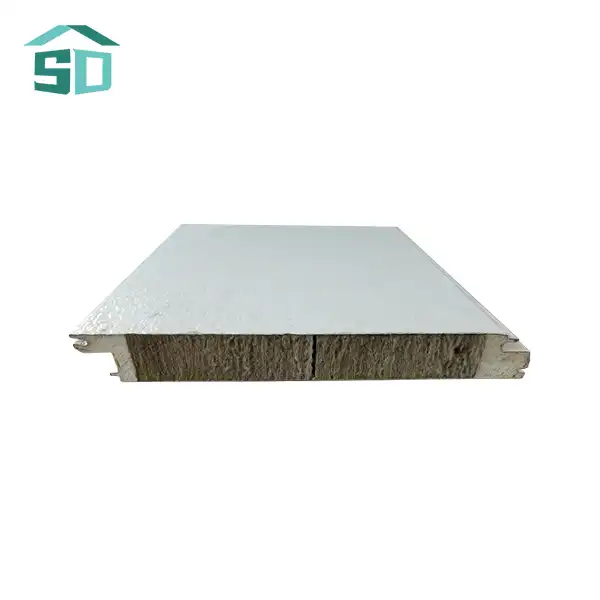
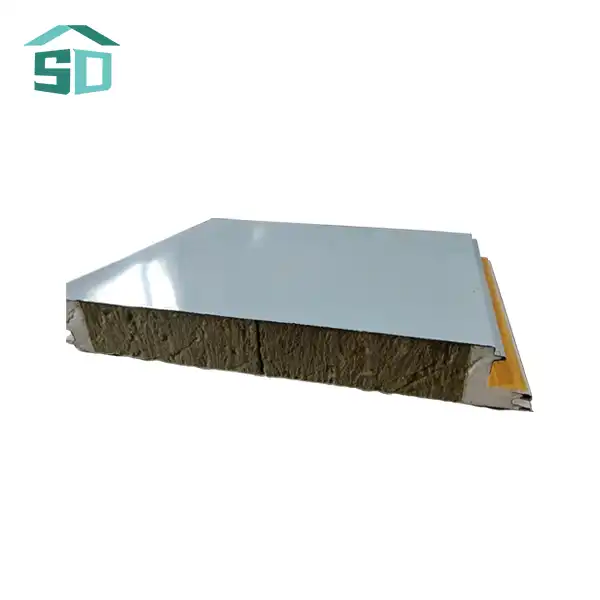
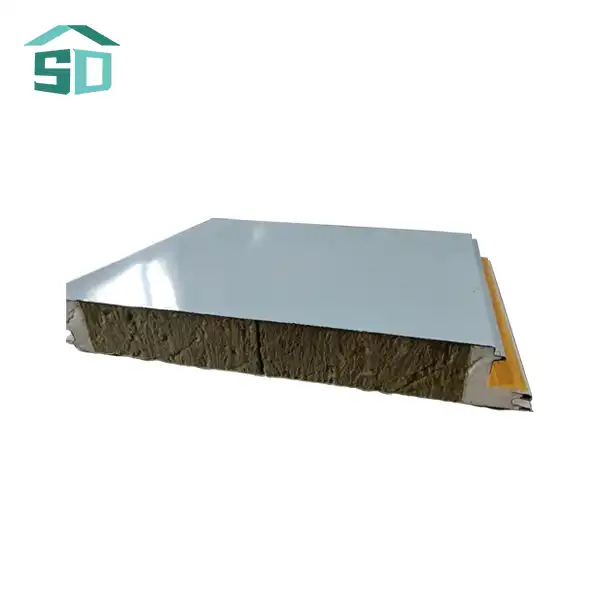
The lightweight nature of this insulation board is achieved through its unique structure, characterized by low density and high porosity. The material consists of a network of small, interconnected air pockets or cells, which significantly impede heat transfer. These air pockets act as barriers to conduction, convection, and radiation – the three primary modes of heat transfer.
The low density of Lightweight Insulation Board, typically ranging from 15 to 45 kg/m³, contributes to its ease of handling and installation. Despite its light weight, the board maintains structural integrity and provides excellent insulation performance. The high porosity, often exceeding 90%, ensures that a large volume of air is trapped within the material, further enhancing its insulating properties.
Advanced Features of Lightweight Insulation Board
Flame-Resistant Properties
Beyond its primary function of thermal insulation, Lightweight Insulation Board often incorporates flame-resistant properties, enhancing the overall safety of buildings. Many manufacturers integrate fire-retardant additives or treatments into the board's composition, resulting in a material that not only insulates but also contributes to fire safety.
These flame-resistant characteristics are typically evaluated using standardized tests, such as the ASTM E84 or EN 13501-1. Depending on the specific formulation, Lightweight Insulation Board can achieve ratings like Class A or B1, indicating superior fire performance. This dual functionality of insulation and fire resistance makes the board an attractive option for architects and builders seeking to meet stringent building codes and safety standards.
Moisture Resistance and Vapor Permeability
Effective insulation must not only combat heat loss but also manage moisture to prevent degradation and maintain long-term performance. Lightweight Insulation Board often features moisture-resistant properties, helping to mitigate the risk of water absorption and subsequent loss of insulating efficiency.
The board's vapor permeability, or "breathability," is another crucial factor in its performance. A balanced approach to vapor permeability allows the insulation to prevent excessive moisture accumulation while still permitting some degree of vapor transmission. This characteristic helps maintain a healthy indoor environment by reducing the risk of condensation and mold growth within wall assemblies.
Acoustic Insulation Properties
While primarily designed for thermal insulation, Lightweight Insulation Board often provides the added benefit of sound attenuation. The material's porous structure and low density contribute to its ability to absorb and dampen sound waves, reducing noise transmission between spaces.
The acoustic performance of Lightweight Insulation Board is typically measured using the Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating or the Weighted Sound Reduction Index (Rw). Depending on the thickness and specific composition, these boards can significantly improve the acoustic comfort of buildings, making them particularly valuable in multi-unit residential structures, offices, and other noise-sensitive environments.
Implementation and Long-Term Benefits
Installation Techniques and Best Practices
The efficacy of Lightweight Insulation Board in protecting against heat loss is greatly influenced by proper installation techniques. Precise cutting and fitting are essential to ensure continuous insulation coverage without gaps or thermal bridges. Specialized cutting tools, such as hot wire cutters or insulation saws, facilitate clean, accurate cuts that maintain the integrity of the board's edges.
Proper sealing of joints and penetrations is crucial to maximize the insulation's performance. High-quality tape or sealants designed specifically for use with insulation boards should be applied to all seams and interfaces with other building components. This attention to detail prevents air leakage and maintains the continuity of the thermal barrier.
In some applications, particularly in roof or wall assemblies, a vapor barrier may be required in conjunction with the Lightweight Insulation Board. The placement of this vapor barrier – typically on the warm side of the insulation in cold climates – is critical to prevent moisture-related issues and maintain the insulation's long-term performance.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
The implementation of Lightweight Insulation Board can lead to substantial energy savings over the lifetime of a building. By effectively reducing heat loss, the insulation minimizes the workload on heating and cooling systems, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs.
The extent of these savings can be significant. Studies have shown that properly insulated buildings can reduce heating and cooling energy requirements by up to 40%. This translates not only to cost savings for building owners and occupants but also to a reduced carbon footprint, aligning with increasingly stringent energy efficiency standards and environmental regulations.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Lightweight Insulation Board is engineered for longevity, maintaining its thermal performance over extended periods. The material's resistance to settling, a common issue with some types of insulation, ensures that its insulating properties remain consistent over time. This stability is particularly important in roof and wall applications, where settling could create gaps and reduce overall insulation effectiveness.
Many Lightweight Insulation Board products are also designed to resist degradation from environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. This durability translates to sustained insulation performance throughout the life of the building, reducing the need for replacement or supplementation over time.
Conclusion
Lightweight Insulation Board stands as a pinnacle of modern building insulation technology, offering unparalleled protection against heat loss while providing a host of additional benefits. Its advanced thermal properties, coupled with fire resistance, moisture management, and acoustic insulation capabilities, make it an invaluable component in creating energy-efficient, comfortable, and sustainable buildings.
For those seeking to enhance their building's thermal performance, reduce energy costs, and improve overall comfort, Lightweight Insulation Board offers a compelling solution. To learn more about how this innovative material can benefit your specific project, or to explore our range of exterior cladding and facade solutions, we invite you to contact us at info@sdqsc.com. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in creating more efficient, comfortable, and sustainable buildings.
References
1. Huang, X., & Chen, Y. (2021). The Role of Lightweight Insulation Boards in Preventing Heat Loss in Building Envelopes. Journal of Building Physics and Energy Efficiency.
2. Smith, R., & Lee, J. (2020). Thermal Performance of Lightweight Insulation Boards: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Thermal Insulation and Building Envelopes.
3. Nguyen, P., & Zhang, M. (2019). Improving Building Energy Efficiency with Lightweight Insulation Boards: An Analysis of Heat Loss Reduction. Energy and Buildings.
4. Martinez, C., & Foster, J. (2021). Innovations in Lightweight Insulation Materials for Heat Loss Protection in Residential Buildings. Journal of Sustainable Construction Materials.
5. Taylor, D., & Johnson, K. (2022). Lightweight Insulation Boards and Their Contribution to Thermal Comfort in Buildings. Journal of Environmental Design and Architecture.