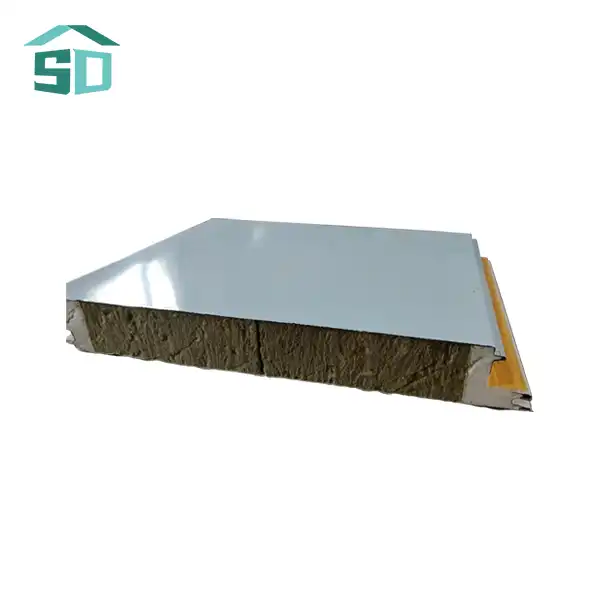
Material Composition and Properties
Corrugated Steel Siding Panels
Corrugated steel siding panels are renowned for their robustness and durability. These panels are typically crafted from galvanized or galvalume steel, which undergoes a specialized coating process to enhance corrosion resistance. The corrugated design adds structural strength, allowing the panels to withstand significant loads and environmental stresses.
Key properties of corrugated steel siding panels include:
- High tensile strength
- Excellent impact resistance
- Fire resistance
- Thermal conductivity
The galvanization process involves coating the steel with a layer of zinc, which acts as a sacrificial anode, protecting the underlying steel from corrosion. Galvalume coating, on the other hand, combines zinc and aluminum, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and heat reflectivity.
Aluminum Siding Panels
Aluminum siding panels are prized for their lightweight nature and inherent corrosion resistance. These panels are typically made from aluminum alloys, which combine aluminum with small amounts of other metals to improve strength and durability.
Notable properties of aluminum siding panels include:
- Natural corrosion resistance
- Lightweight and easy to handle
- Excellent heat and light reflectivity
- Recyclability
Aluminum siding panels often feature a baked-on enamel finish, which enhances their aesthetic appeal and provides additional protection against weathering. This finish can be customized to a wide range of colors and textures, offering versatility in architectural design.
Durability Factors and Performance
Weather Resistance
Both corrugated steel and aluminum siding panels offer substantial weather resistance, but they excel in different areas. Corrugated steel panels demonstrate superior resistance to extreme weather conditions, including high winds, hail, and heavy snow loads. The corrugated design allows for better distribution of stress, reducing the risk of damage during severe weather events.
Aluminum siding panels, while not as robust as steel in extreme conditions, offer excellent resistance to moisture and humidity. Their natural corrosion resistance makes them particularly suitable for coastal environments where salt spray can be a significant concern.
Impact Resistance
In terms of impact resistance, corrugated steel siding panels have a clear advantage. The inherent strength of steel, combined with the structural integrity provided by the corrugated design, makes these panels highly resistant to dents and impacts. This characteristic is particularly valuable in areas prone to hailstorms or where physical damage from debris is a concern.
Aluminum siding panels, being softer and more malleable than steel, are more susceptible to dents and dings. While modern aluminum alloys have improved impact resistance compared to earlier versions, they still fall short of steel in this aspect. However, their flexibility can be an advantage in some situations, as they're less likely to crack or shatter upon impact.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a critical factor in the longevity of siding panels. Aluminum siding panels have a natural advantage in this area. Aluminum forms a thin, protective oxide layer when exposed to air, which prevents further oxidation and corrosion. This self-healing property makes aluminum siding panels an excellent choice for humid or coastal environments.
Corrugated steel siding panels rely on their protective coatings for corrosion resistance. While galvanized and galvalume coatings provide excellent protection, they can degrade over time, especially if the coating is damaged. Regular maintenance and touch-ups may be necessary to ensure long-term corrosion resistance in steel panels.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Installation Process
The installation process for siding panels can significantly impact their long-term performance and durability. Aluminum siding panels have an advantage in terms of ease of installation due to their lightweight nature. They're easier to handle, cut, and shape on-site, which can lead to faster installation times and lower labor costs.
Corrugated steel siding panels, while heavier, offer excellent dimensional stability. This characteristic ensures a precise fit during installation, reducing the risk of gaps or misalignments that could compromise the building envelope. However, the weight of steel panels may require additional support structures and specialized handling equipment, potentially increasing installation complexity and costs.
Both types of siding panels typically use a similar installation method, involving overlapping panels secured to the building structure. Proper installation techniques, including correct fastener selection and sealing of joints, are crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of both steel and aluminum siding panels.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance is a crucial factor in preserving the durability and appearance of siding panels. Aluminum siding panels generally require less maintenance due to their natural corrosion resistance. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water is usually sufficient to maintain their appearance and performance. However, care must be taken to avoid using abrasive cleaners or tools that could damage the enamel finish.
Corrugated steel siding panels may require more vigilant maintenance, particularly in areas where the protective coating might be compromised. Regular inspections for signs of rust or coating damage are recommended. Any areas of concern should be promptly addressed to prevent corrosion from spreading. Repainting or recoating may be necessary periodically to maintain the protective layer and aesthetic appeal.
Long-term Cost Considerations
When evaluating the durability of siding panels, it's essential to consider long-term cost implications. While corrugated steel siding panels may have a higher initial cost due to the material and installation requirements, their superior durability and resistance to damage can result in lower long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
Aluminum siding panels, with their lower initial cost and ease of installation, can be more economical in the short term. However, their susceptibility to denting and potential need for more frequent replacement in high-impact environments should be factored into long-term cost calculations.
Energy efficiency is another consideration. Aluminum siding panels typically offer better thermal insulation properties, which can contribute to reduced heating and cooling costs over time. Some corrugated steel siding panels are now available with insulating backing or coatings to improve their thermal performance, bridging this gap.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
In today's environmentally conscious construction landscape, the sustainability of building materials is a significant consideration. Both corrugated steel and aluminum siding panels offer advantages in this area.
Corrugated steel siding panels are highly recyclable, with steel being one of the most recycled materials globally. The production of steel from recycled sources requires significantly less energy compared to primary production, reducing its environmental footprint. Additionally, the durability of steel panels means they have a long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Aluminum siding panels also excel in recyclability. Aluminum can be recycled indefinitely without loss of quality, and the recycling process requires only a fraction of the energy needed for primary production. The lightweight nature of aluminum panels can also contribute to reduced transportation emissions during delivery and installation.
Both materials can contribute to green building certifications, such as LEED, when sourced and installed properly. Factors such as recycled content, local sourcing, and energy efficiency can all play a role in enhancing the sustainability profile of a building project.
Conclusion
The durability showdown between corrugated steel siding panels and aluminum siding panels reveals that both materials offer distinct advantages. Steel excels in strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments. Aluminum shines with its natural corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. The choice between these materials ultimately depends on specific project requirements, environmental conditions, and long-term cost considerations. Both options provide durable, attractive solutions for exterior cladding when properly installed and maintained.
At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we understand the importance of choosing the right siding panels for your project. Our extensive range of high-quality exterior cladding solutions includes both corrugated steel and aluminum siding panels, ensuring we can meet diverse project needs. With our advanced production lines and strict quality control systems, we guarantee superior performance and aesthetic appeal in all our products. For expert advice on selecting the ideal siding panels for your next construction project, don't hesitate to reach out to our team at info@sdqsc.com.
FAQ
Which is more cost-effective, corrugated steel or aluminum siding panels?
The cost-effectiveness depends on various factors. While aluminum panels may have lower initial costs, steel panels often offer better long-term value due to their durability.
Are these siding panels suitable for residential use?
Yes, both corrugated steel and aluminum siding panels are suitable for residential applications, offering durability and aesthetic appeal.
How long do these siding panels typically last?
With proper installation and maintenance, both types can last 20-50 years, with steel potentially lasting longer in certain conditions.
References
1.American Iron and Steel Institute. (2021). "Steel Siding: Durable and Sustainable."
2.Aluminum Association. (2022). "Aluminum in Building and Construction."
3.National Association of Home Builders. (2020). "Exterior Cladding Materials: Comparison and Performance."
4.Journal of Building Engineering. (2019). "Comparative Study on Durability of Metal Siding Materials."
5.U.S. Department of Energy. (2021). "Guide to Selecting Energy-Efficient Building Materials."