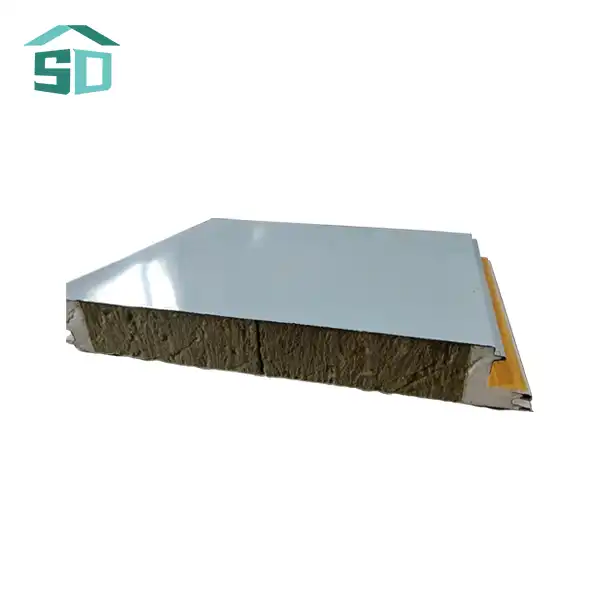
Grasping the Composition and Properties of PU Insulation Boards
The Science Behind Closed-Cell Technology
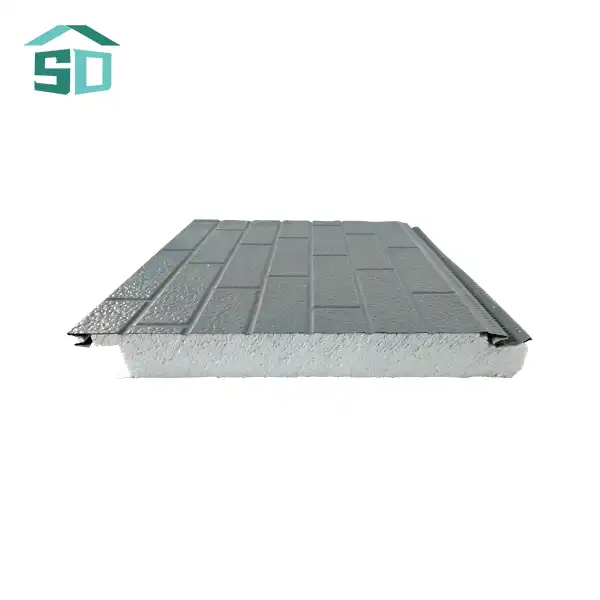
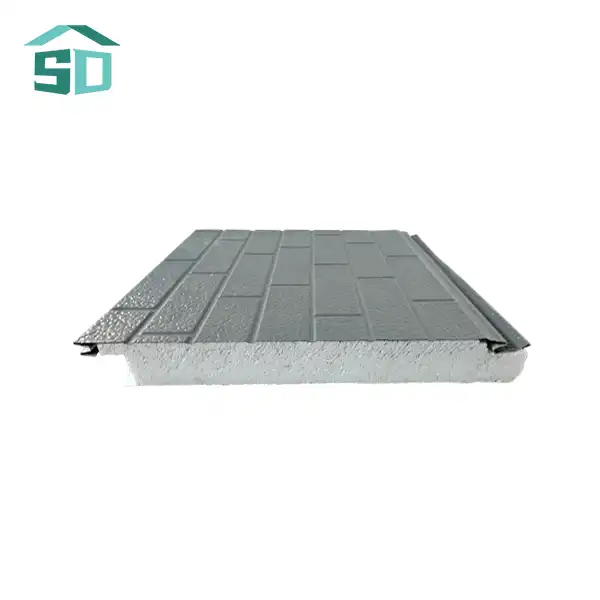
PU insulation boards owe their remarkable performance to the innovative closed-cell technology. This structure consists of millions of microscopic cells, each filled with a low-conductivity gas. The cell walls are impermeable, preventing the gas from escaping and maintaining the insulation's effectiveness over time. This unique composition results in a material with exceptional thermal resistance, capable of significantly reducing heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors.
The closed-cell structure of PU insulation boards also contributes to their high compressive strength. This property allows the boards to withstand substantial pressure without deforming, making them suitable for use in load-bearing applications. The dense cellular matrix provides excellent dimensional stability, ensuring that the boards maintain their shape and performance even under varying temperature and humidity conditions.
Thermal Conductivity and R-Value
One of the key advantages of PU insulation boards is their low thermal conductivity. With a thermal conductivity value as low as 0.022 W/m·K, these boards outperform many traditional insulation materials. This low conductivity translates to a high R-value, which measures the material's resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation performance.
PU insulation boards typically offer R-values ranging from R-5 to R-7 per inch of thickness, depending on the specific formulation. This high insulation efficiency allows for thinner insulation layers compared to other materials, maximizing usable space in buildings while still meeting or exceeding energy efficiency standards.
Moisture Resistance and Vapor Permeability
The closed-cell structure of PU insulation boards provides excellent moisture resistance. Unlike open-cell foams or fibrous insulation materials, closed-cell PU boards have a low water absorption rate and high resistance to water vapor transmission. This property helps prevent moisture accumulation within the insulation layer, reducing the risk of mold growth and maintaining the insulation's thermal performance over time.
The vapor permeability of PU insulation boards can be tailored to suit specific applications. Some formulations offer a higher degree of vapor permeability, allowing for controlled moisture movement in wall assemblies. Others provide a near-impermeable barrier, making them ideal for use in high-humidity environments or as part of a vapor control strategy in building envelopes.
Applications and Benefits of PU Insulation Boards in Construction
Versatility in Building Applications
PU insulation boards find widespread use in various construction applications due to their versatility and superior performance. In residential construction, these boards are commonly used for insulating walls, roofs, and floors. Their high insulation value allows for thinner wall assemblies, maximizing living space while meeting energy efficiency requirements.
In commercial and industrial buildings, PU insulation boards are often used in flat or low-slope roofing systems. Their excellent moisture resistance and compressive strength make them ideal for use in inverted roof assemblies or as part of a tapered insulation system for proper drainage. The boards' compatibility with various roofing membranes and adhesives further enhances their versatility in roofing applications.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
The superior thermal performance of PU insulation boards translates to significant energy savings for building owners. By effectively reducing heat transfer through the building envelope, these boards help maintain consistent indoor temperatures, reducing the load on heating and cooling systems. This improved energy efficiency not only lowers utility costs but also contributes to a building's overall sustainability profile.
The long-term durability of PU insulation boards also offers cost benefits. Their resistance to moisture, dimensional stability, and minimal degradation over time ensure that the insulation maintains its performance throughout the building's lifespan. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacement or maintenance, providing long-term value for property owners.
Fire Safety and Building Code Compliance
Modern PU insulation boards are formulated with fire-retardant additives to enhance their safety profile. Many products meet stringent fire safety standards, achieving classifications such as Class B1 (non-combustible) in fire resistance tests. This fire performance, combined with their excellent insulation properties, makes PU insulation boards a preferred choice for meeting building code requirements related to energy efficiency and fire safety.
The use of PU insulation boards can also contribute to achieving higher ratings in green building certification programs such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). Their energy-saving properties, potential for recycled content, and ability to reduce overall material use in construction align well with sustainability criteria in these certification systems.
Installation Techniques and Best Practices for PU Insulation Boards
Preparation and Handling
Proper installation of PU insulation boards begins with careful preparation and handling. The boards should be stored in a dry, protected area prior to installation to prevent moisture absorption. Before installation, ensure that the substrate is clean, dry, and free from debris. Any existing moisture issues in the building structure should be addressed before applying the insulation.
PU insulation boards are relatively lightweight and easy to handle, but care should be taken to avoid damaging the edges or corners during transport and installation. Many manufacturers offer boards with shiplap or tongue-and-groove edges to facilitate proper alignment and minimize thermal bridging at the joints.
Cutting and Fitting
PU insulation boards can be easily cut to size using standard tools such as utility knives, saws, or hot-wire cutters. When cutting, it's important to maintain straight edges to ensure tight-fitting joints between boards. For complex shapes or penetrations, templates can be used to achieve precise cuts. Any gaps or voids should be filled with compatible spray foam insulation to maintain the continuity of the thermal barrier.
When installing PU insulation boards in wall cavities, it's crucial to ensure a snug fit without compressing the board. Compression can reduce the insulation's effectiveness and potentially lead to bowing of the wall surface. In some applications, such as external wall insulation systems, mechanical fasteners may be used in conjunction with adhesives to secure the boards.
Sealing and Vapor Control
Proper sealing of joints and penetrations is essential to maximize the performance of PU insulation boards. Specialized tapes or sealants designed for use with polyurethane insulation should be used to seal the joints between boards. This sealing not only enhances thermal performance but also contributes to the overall air and moisture barrier of the building envelope.
In applications where vapor control is critical, such as in cold storage facilities or in climates with significant temperature differentials, additional vapor barrier materials may be required. The placement of vapor barriers in relation to the PU insulation boards should be carefully considered based on the specific climate and building design to prevent moisture accumulation within the wall or roof assembly.
Conclusion
PU insulation boards represent a significant advancement in building insulation technology, offering a unique combination of high thermal performance, moisture resistance, and versatility. Their closed-cell structure provides superior insulation properties, allowing for thinner wall assemblies and improved energy efficiency in buildings. From residential construction to commercial and industrial applications, PU insulation boards have proven their value in creating more sustainable, comfortable, and energy-efficient structures.
At Weifang Sandong Building Materials Co., Ltd., we are committed to providing high-quality PU insulation boards that meet the diverse needs of the construction industry. Our products are engineered to deliver exceptional thermal performance, durability, and ease of installation. Whether you're working on a new construction project or retrofitting an existing building, our PU insulation boards offer a reliable solution for achieving your energy efficiency and sustainability goals. To learn more about our products and how they can benefit your next project, please contact us at info@sdqsc.com.
FAQ
What makes PU insulation boards different from other insulation materials?
PU insulation boards feature a unique closed-cell structure that provides superior thermal resistance, moisture resistance, and compressive strength compared to many traditional insulation materials.
Are PU insulation boards environmentally friendly?
Modern PU insulation boards are manufactured with eco-friendly blowing agents and can contribute to energy savings in buildings, aligning with sustainability goals.
How long do PU insulation boards last?
PU insulation boards are known for their durability and can maintain their performance for the lifetime of the building when properly installed and protected.
References
1.Polyurethane Foam Association. (2021). "Technical Bulletin: Thermal Performance of Polyurethane and Polyisocyanurate Foam Insulation."
2.Building Science Corporation. (2019). "Guide to Insulating Sheathing."
3.International Energy Agency. (2020). "Energy Efficiency in Buildings: Technology Solutions and Market Progress."
4.National Institute of Building Sciences. (2018). "Whole Building Design Guide: Building Envelope Design Guide."